Page 13 - Review of Medical Microbiology and Immunology ( PDFDrive )
P. 13
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com 1 Viruses Bacteria mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com
PART I Basic Bacteriology
2
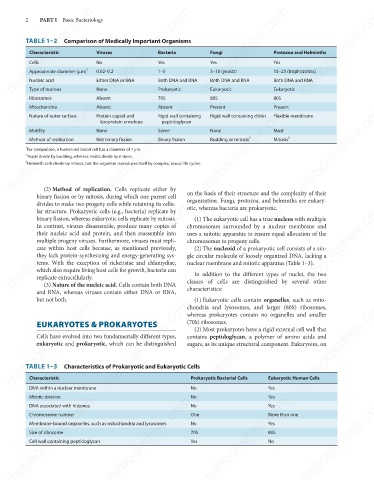
TABLE 1–2 Comparison of Medically Important Organisms
Characteristic
Protozoa and Helminths
Fungi
Yes
Cells
Yes
No
Yes
3–10 (yeasts)
1–5
15–25 (trophozoites)
0.02–0.2
Approximate diameter (μm)
Nucleic acid
Eukaryotic
Eukaryotic
None
Type of nucleus
Prokaryotic
80S
80S
Absent
70S
Ribosomes Either DNA or RNA Both DNA and RNA Both DNA and RNA Both DNA and RNA
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com None mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com 3 mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com
Absent
Present
Absent
Present
Mitochondria
Rigid wall containing
Nature of outer surface
Flexible membrane
Protein capsid and
Rigid wall containing chitin
lipoprotein envelope
peptidoglycan
Most
Some
Motility
None
2
Budding or mitosis
Binary fission
Mitosis
Method of replication
Not binary fission
1
For comparison, a human red blood cell has a diameter of 7 μm.
2
Yeasts divide by budding, whereas molds divide by mitosis.
3
Helminth cells divide by mitosis, but the organism reproduces itself by complex, sexual life cycles.
(2) Method of replication. Cells replicate either by
binary fission or by mitosis, during which one parent cell on the basis of their structure and the complexity of their
organization. Fungi, protozoa, and helminths are eukary-
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com chromosomes surrounded by a nuclear membrane and mebooksfree.com
divides to make two progeny cells while retaining its cellu-
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
otic, whereas bacteria are prokaryotic.
lar structure. Prokaryotic cells (e.g., bacteria) replicate by
binary fission, whereas eukaryotic cells replicate by mitosis.
(1) The eukaryotic cell has a true nucleus with multiple
In contrast, viruses disassemble, produce many copies of
uses a mitotic apparatus to ensure equal allocation of the
their nucleic acid and protein, and then reassemble into
multiple progeny viruses. Furthermore, viruses must repli-
chromosomes to progeny cells.
(2) The nucleoid of a prokaryotic cell consists of a sin-
cate within host cells because, as mentioned previously,
gle circular molecule of loosely organized DNA, lacking a
they lack protein-synthesizing and energy-generating sys-
tems. With the exception of rickettsiae and chlamydiae,
nuclear membrane and mitotic apparatus (Table 1–3).
which also require living host cells for growth, bacteria can
In addition to the different types of nuclei, the two
replicate extracellularly.
(3) Nature of the nucleic acid. Cells contain both DNA
characteristics:
and RNA, whereas viruses contain either DNA or RNA, classes of cells are distinguished by several other
but not both.
(1) Eukaryotic cells contain organelles, such as mito-
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com (70S) ribosomes. Eukaryotic Human Cells mebooksfree.com
chondria and lysosomes, and larger (80S) ribosomes,
whereas prokaryotes contain no organelles and smaller
EUKARYOTES & PROKARYOTES
(2) Most prokaryotes have a rigid external cell wall that
Cells have evolved into two fundamentally different types,
contains peptidoglycan, a polymer of amino acids and
sugars, as its unique structural component. Eukaryotes, on
eukaryotic and prokaryotic, which can be distinguished
TABLE 1–3 Characteristics of Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells
Characteristic
Prokaryotic Bacterial Cells
Yes
DNA within a nuclear membrane
No
Mitotic division
Yes
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com No mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com
No
Yes
DNA associated with histones
Chromosome number
One
More than one
No
Membrane-bound organelles, such as mitochondria and lysosomes
Yes
70S
Size of ribosome
80S
Cell wall containing peptidoglycan
Yes
No
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com