Page 17 - Review of Medical Microbiology and Immunology ( PDFDrive )
P. 17
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com Chemical Composition Function mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
PART I Basic Bacteriology
6
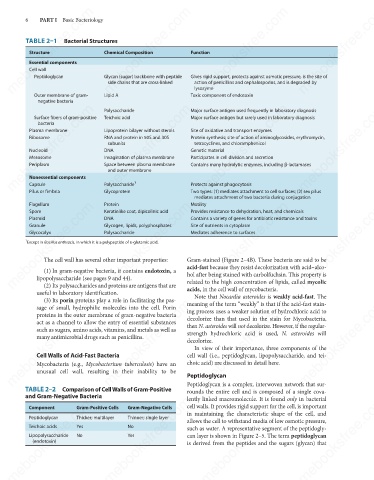
TABLE 2–1 Bacterial Structures
Structure
Essential components
Cell wall
Peptidoglycan
action of penicillins and cephalosporins, and is degraded by
side chains that are cross-linked
lysozyme
Outer membrane of gram-
Lipid A
Toxic component of endotoxin
negative bacteria Glycan (sugar) backbone with peptide Gives rigid support, protects against osmotic pressure, is the site of
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com Lipoprotein bilayer without sterols Site of oxidative and transport enzymes mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
Major surface antigen used frequently in laboratory diagnosis
Polysaccharide
Teichoic acid
Surface fibers of gram-positive
Major surface antigen but rarely used in laboratory diagnosis
bacteria
Plasma membrane
Ribosome
RNA and protein in 50S and 30S
Protein synthesis; site of action of aminoglycosides, erythromycin,
subunits
tetracyclines, and chloramphenicol
DNA
Nucleoid
Genetic material
Invagination of plasma membrane
Mesosome
Participates in cell division and secretion
Periplasm
Contains many hydrolytic enzymes, including β-lactamases
Space between plasma membrane
and outer membrane
Nonessential components
1
Protects against phagocytosis
Polysaccharide
Capsule
Two types: (1) mediates attachment to cell surfaces; (2) sex pilus
Glycoprotein
Pilus or fimbria
mediates attachment of two bacteria during conjugation
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com Glycogen, lipids, polyphosphates Gram-stained (Figure 2–4B). These bacteria are said to be mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
Protein
Motility
Flagellum
Spore
Provides resistance to dehydration, heat, and chemicals
Keratinlike coat, dipicolinic acid
DNA
Contains a variety of genes for antibiotic resistance and toxins
Plasmid
Granule
Site of nutrients in cytoplasm
Glycocalyx
Mediates adherence to surfaces
Polysaccharide
1
Except in Bacillus anthracis, in which it is a polypeptide of d-glutamic acid.
The cell wall has several other important properties:
acid-fast because they resist decolorization with acid–alco-
(1) In gram-negative bacteria, it contains endotoxin, a
lipopolysaccharide (see pages 9 and 44).
related to the high concentration of lipids, called mycolic
(2) Its polysaccharides and proteins are antigens that are
acids, in the cell wall of mycobacteria.
useful in laboratory identification. hol after being stained with carbolfuchsin. This property is
Note that Nocardia asteroides is weakly acid-fast. The
(3) Its porin proteins play a role in facilitating the pas-
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com decolorize than that used in the stain for Mycobacteria, mebooksfree.com
meaning of the term “weakly” is that if the acid-fast stain-
sage of small, hydrophilic molecules into the cell. Porin
ing process uses a weaker solution of hydrochloric acid to
proteins in the outer membrane of gram-negative bacteria
act as a channel to allow the entry of essential substances
then N. asteroides will not decolorize. However, if the regular-
such as sugars, amino acids, vitamins, and metals as well as
strength hydrochloric acid is used, N. asteroides will
many antimicrobial drugs such as penicillins.
decolorize.
In view of their importance, three components of the
cell wall (i.e., peptidoglycan, lipopolysaccharide, and tei-
Cell Walls of Acid-Fast Bacteria
choic acid) are discussed in detail here.
Mycobacteria (e.g., Mycobacterium tuberculosis) have an
unusual cell wall, resulting in their inability to be
Peptidoglycan is a complex, interwoven network that sur-
TABLE 2–2 Comparison of Cell Walls of Gram-Positive Peptidoglycan
rounds the entire cell and is composed of a single cova-
and Gram-Negative Bacteria
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com allows the cell to withstand media of low osmotic pressure, mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
lently linked macromolecule. It is found only in bacterial
cell walls. It provides rigid support for the cell, is important
Gram-Negative Cells
Component
Gram-Positive Cells
in maintaining the characteristic shape of the cell, and
Peptidoglycan
Thinner; single layer
Thicker; multilayer
Yes
No
Teichoic acids
such as water. A representative segment of the peptidogly-
can layer is shown in Figure 2–5. The term peptidoglycan
Lipopolysaccharide
No
Yes
(endotoxin)
is derived from the peptides and the sugars (glycan) that
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com