Page 267 - Review of Medical Microbiology and Immunology ( PDFDrive )
P. 267
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com Bloodstream: mebooksfree.com the virus damaging or killing the infected cell. For example, mebooksfree.com
PART III Basic Virology
256
However, there are some diseases that are not caused by
Day
Small intestine:
Invasion
multiplication
0
rotavirus-induced diarrhea is caused primarily by stimula-
tion of the enteric nervous system. It is thought that the
rotavirus-infected enterocytes produce cytokines that stim-
Mesenteric lymph nodes:
1
Multiplication
electrolyte secretion into the bowel lumen.
2
There are other diseases in which cell killing by immu-
nologic attack plays an important role in pathogenesis.
Primary viremia ulate the enteric neurons, resulting in excess fluid and
Both cytotoxic T cells and antibodies play a role in
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com Bloodstream: gitis (LCM) in mice; LCM occurs in humans also but is quite mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
3
immunopathogenesis.
Central focus of
multiplication (liver, spleen)
(1) The best-studied system is lymphocytic choriomenin-
4
rare. When LCM virus is inoculated into the brain of an
Secondary viremia
adult mouse, virus replication occurs and death follows.
5
Initial antibody appearance
However, when LCM virus is inoculated into the brain of an
immunosuppressed adult mouse or a newborn mouse, the
6
animal remains well despite extensive virus replication.
CNS:
Invasion and
When immune lymphocytes are inoculated into these
multiplication
infected, but otherwise healthy mice, death ensues. It appears
resulting in
7
that death of the cells is caused by immune attack by cyto-
meningoencephalitis
toxic T cells on the new viral antigens in the cell membrane
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com High level of viruses do not cause a CPE, and the damage to the hepato- mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
rather than by virus-induced inhibition of cell functions.
8
(2) Cytotoxic T cells are involved in the pathogenesis
of hepatitis caused by hepatitis A, B, and C viruses. These
9
cytes is the result of the recognition of viral antigens on the
hepatocyte surface by cytotoxic T cells. The rash of measles
10
is similarly caused by these cells attacking the infected vas-
antibody in serum
cular endothelium in the skin.
1
11
Paralysis caused by death
(3) Immune-mediated pathogenesis also occurs when
of motor neurons
deposited in various tissues. This occurs in hepatitis B
12
Excretion in feces
virus infection, in which immune complexes play a role in
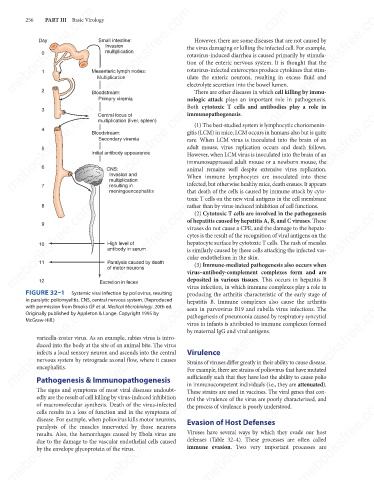
FIGURE 32–1 Systemic viral infection by poliovirus, resulting virus–antibody-complement complexes form and are
producing the arthritis characteristic of the early stage of
in paralytic poliomyelitis. CNS, central nervous system. (Reproduced
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com virus in infants is attributed to immune complexes formed mebooksfree.com
hepatitis B. Immune complexes also cause the arthritis
mebooksfree.com
with permission from Brooks GF et al. Medical Microbiology. 20th ed.
seen in parvovirus B19 and rubella virus infections. The
Originally published by Appleton & Lange. Copyright 1995 by
pathogenesis of pneumonia caused by respiratory syncytial
McGraw-Hill.)
by maternal IgG and viral antigens.
varicella-zoster virus. As an example, rabies virus is intro-
duced into the body at the site of an animal bite. The virus
Virulence
infects a local sensory neuron and ascends into the central
nervous system by retrograde axonal flow, where it causes
Strains of viruses differ greatly in their ability to cause disease.
encephalitis.
sufficiently such that they have lost the ability to cause polio
Pathogenesis & Immunopathogenesis
in immunocompetent individuals (i.e., they are attenuated).
The signs and symptoms of most viral diseases undoubt- For example, there are strains of poliovirus that have mutated
These strains are used in vaccines. The viral genes that con-
edly are the result of cell killing by virus-induced inhibition
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com Evasion of Host Defenses mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com
trol the virulence of the virus are poorly characterized, and
of macromolecular synthesis. Death of the virus-infected
the process of virulence is poorly understood.
cells results in a loss of function and in the symptoms of
disease. For example, when poliovirus kills motor neurons,
paralysis of the muscles innervated by those neurons
Viruses have several ways by which they evade our host
results. Also, the hemorrhages caused by Ebola virus are
defenses (Table 32–4). These processes are often called
due to the damage to the vascular endothelial cells caused
immune evasion. Two very important processes are
by the envelope glycoprotein of the virus.
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com