Page 284 - Review of Medical Microbiology and Immunology ( PDFDrive )
P. 284
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com Herpesvirus-encoded ACV-MP Cellular mebooksfree.com ACV-TP mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com
273
CHAPTER 35 Antiviral Drugs
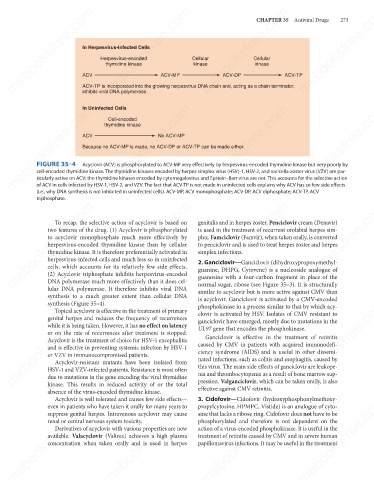
In Herpesvirus-Infected Cells
Cellular
thymidine kinase
kinase
kinase
ACV
ACV-DP
ACV-TP is incorporated into the growing herpesvirus DNA chain and, acting as a chain terminator,
inhibits viral DNA polymerase.
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com thymidine kinase No ACV-MP mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com
In Uninfected Cells
Cell-encoded
ACV
Because no ACV-MP is made, no ACV-DP or ACV-TP can be made either.
FIGURE 35–4
Acyclovir (ACV) is phosphorylated to ACV-MP very effectively by herpesvirus-encoded thymidine kinase but very poorly by
cell-encoded thymidine kinase. The thymidine kinases encoded by herpes simplex virus (HSV)-1, HSV-2, and varicella-zoster virus (VZV) are par-
ticularly active on ACV; the thymidine kinases encoded by cytomegalovirus and Epstein–Barr virus are not. This accounts for the selective action
of ACV in cells infected by HSV-1, HSV-2, and VZV. The fact that ACV-TP is not made in uninfected cells explains why ACV has so few side effects
(i.e., why DNA synthesis is not inhibited in uninfected cells). ACV-MP, ACV monophosphate; ACV-DP, ACV diphosphate; ACV-TP, ACV
triphosphate.
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com genitalis and in herpes zoster. Penciclovir cream (Denavir) mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
To recap, the selective action of acyclovir is based on
two features of the drug. (1) Acyclovir is phosphorylated
is used in the treatment of recurrent orolabial herpes sim-
to acyclovir monophosphate much more effectively by
plex. Famciclovir (Famvir), when taken orally, is converted
herpesvirus-encoded thymidine kinase than by cellular
to penciclovir and is used to treat herpes zoster and herpes
simplex infections.
thymidine kinase. It is therefore preferentially activated in
herpesvirus-infected cells and much less so in uninfected
2. Ganciclovir—Ganciclovir (dihydroxypropoxymethyl-
cells, which accounts for its relatively few side effects.
guanine, DHPG, Cytovene) is a nucleoside analogue of
(2) Acyclovir triphosphate inhibits herpesvirus-encoded
DNA polymerase much more effectively than it does cel-
normal sugar, ribose (see Figure 35–3). It is structurally
lular DNA polymerase. It therefore inhibits viral DNA
similar to acyclovir but is more active against CMV than
synthesis to a much greater extent than cellular DNA guanosine with a four-carbon fragment in place of the
is acyclovir. Ganciclovir is activated by a CMV-encoded
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com ganciclovir have emerged, mostly due to mutations in the mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
synthesis (Figure 35–4).
phosphokinase in a process similar to that by which acy-
Topical acyclovir is effective in the treatment of primary
clovir is activated by HSV. Isolates of CMV resistant to
genital herpes and reduces the frequency of recurrences
while it is being taken. However, it has no effect on latency
UL97 gene that encodes the phosphokinase.
or on the rate of recurrences after treatment is stopped.
Ganciclovir is effective in the treatment of retinitis
Acyclovir is the treatment of choice for HSV-1 encephalitis
caused by CMV in patients with acquired immunodefi-
and is effective in preventing systemic infection by HSV-1
ciency syndrome (AIDS) and is useful in other dissemi-
or VZV in immunocompromised patients.
nated infections, such as colitis and esophagitis, caused by
Acyclovir-resistant mutants have been isolated from
this virus. The main side effects of ganciclovir are leukope-
HSV-1 and VZV-infected patients. Resistance is most often
due to mutations in the gene encoding the viral thymidine
pression. Valganciclovir, which can be taken orally, is also
kinase. This results in reduced activity of or the total
effective against CMV retinitis.
absence of the virus-encoded thymidine kinase. nia and thrombocytopenia as a result of bone marrow sup-
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com phosphorylated and therefore is not dependent on the mebooksfree.com
3. Cidofovir—Cidofovir (hydroxyphosphonylmethoxy-
mebooksfree.com
Acyclovir is well tolerated and causes few side effects—
mebooksfree.com
even in patients who have taken it orally for many years to
propylcytosine, HPMPC, Vistide) is an analogue of cyto-
suppress genital herpes. Intravenous acyclovir may cause
sine that lacks a ribose ring. Cidofovir does not have to be
renal or central nervous system toxicity.
action of a virus-encoded phosphokinase. It is useful in the
Derivatives of acyclovir with various properties are now
treatment of retinitis caused by CMV and in severe human
available. Valacyclovir (Valtrex) achieves a high plasma
concentration when taken orally and is used in herpes
papillomavirus infections. It may be useful in the treatment
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com