Page 288 - Review of Medical Microbiology and Immunology ( PDFDrive )
P. 288
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com Number of Chapter for 277 mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
CHAPTER 35 Antiviral Drugs
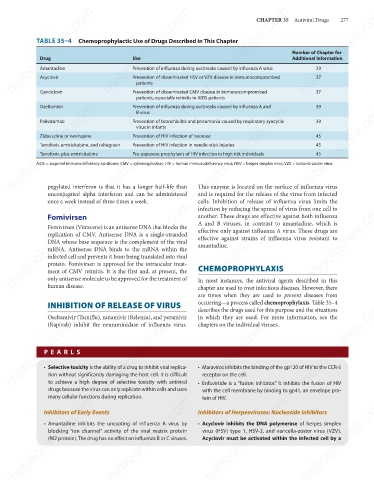
TABLE 35–4 Chemoprophylactic Use of Drugs Described in This Chapter
Additional Information
Use
Drug
39
Prevention of influenza during outbreaks caused by influenza A virus
Amantadine
Prevention of disseminated HSV or VZV disease in immunocompromised
Acyclovir
patients
37
Ganciclovir
Prevention of disseminated CMV disease in immunocompromised
patients, especially retinitis in AIDS patients 37
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com
Oseltamivir
39
Prevention of influenza during outbreaks caused by influenza A and
B virus
39
Prevention of bronchiolitis and pneumonia caused by respiratory syncytial
Palivizumab
virus in infants
Prevention of HIV infection of neonate
Zidovudine or nevirapine
45
Prevention of HIV infection in needle-stick injuries
45
Tenofovir, emtricitabine, and raltegravir
Pre-exposure prophylaxis of HIV infection in high risk individuals
45
Tenofovir, plus emtricitabine
AIDS = acquired immunodeficiency syndrome; CMV = cytomegalovirus; HIV = human immunodeficiency virus; HSV = herpes simplex virus; VZV = varicella-zoster virus.
pegylated interferon is that it has a longer half-life than
unconjugated alpha interferon and can be administered This enzyme is located on the surface of influenza virus
and is required for the release of the virus from infected
once a week instead of three times a week.
cells. Inhibition of release of influenza virus limits the
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com A and B viruses, in contrast to amantadine, which is mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
infection by reducing the spread of virus from one cell to
another. These drugs are effective against both influenza
Fomivirsen
Fomivirsen (Vitravene) is an antisense DNA that blocks the
effective only against influenza A virus. These drugs are
replication of CMV. Antisense DNA is a single-stranded
effective against strains of influenza virus resistant to
DNA whose base sequence is the complement of the viral
amantadine.
mRNA. Antisense DNA binds to the mRNA within the
infected cell and prevents it from being translated into viral
protein. Fomivirsen is approved for the intraocular treat-
CHEMOPROPHYLAXIS
ment of CMV retinitis. It is the first and, at present, the
only antisense molecule to be approved for the treatment of
In most instances, the antiviral agents described in this
human disease.
chapter are used to treat infectious diseases. However, there
are times when they are used to prevent diseases from
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com chapters on the individual viruses. mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
occurring—a process called chemoprophylaxis. Table 35–4
INHIBITION OF RELEASE OF VIRUS
describes the drugs used for this purpose and the situations
Oseltamivir (Tamiflu), zanamivir (Relenza), and peramivir
in which they are used. For more information, see the
(Rapivab) inhibit the neuraminidase of influenza virus.
PEARLS
• Selective toxicity is the ability of a drug to inhibit viral replica-
receptor on the cell.
tion without significantly damaging the host cell. It is difficult
to achieve a high degree of selective toxicity with antiviral
• Enfuvirtide is a “fusion inhibitor.” It inhibits the fusion of HIV
drugs because the virus can only replicate within cells and uses • Maraviroc inhibits the binding of the gp120 of HIV to the CCR-5
with the cell membrane by binding to gp41, an envelope pro-
many cellular functions during replication.
tein of HIV.
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com • Acyclovir inhibits the DNA polymerase of herpes simplex mebooksfree.com
Inhibitors of Herpesviruses: Nucleoside Inhibitors
Inhibitors of Early Events
• Amantadine inhibits the uncoating of influenza A virus by
blocking “ion channel” activity of the viral matrix protein
virus (HSV) type 1, HSV-2, and varicella-zoster virus (VZV).
Acyclovir must be activated within the infected cell by a
(M2 protein). The drug has no effect on influenza B or C viruses.
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com