Page 318 - Review of Medical Microbiology and Immunology ( PDFDrive )
P. 318
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
CHAPTER 38 DNA Nonenveloped Viruses
307
Genital warts are among the most common sexually
transmitted diseases. Skin warts are more common in
children and young adults and tend to regress in older
adults. HPV transmitted from an infected mother to the
neonate during childbirth causes warts in the mouth and in
the respiratory tract, especially on the larynx, of the infant.
Many species of animals are infected with their own types
of papillomaviruses, but these viruses are not an important
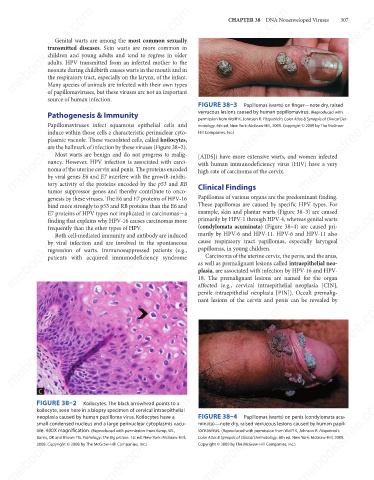
source of human infection. FIGURE 38–3 Papillomas (warts) on finger—note dry, raised
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com matology. 6th ed. New York: McGraw-Hill, 2009. Copyright © 2009 by The McGraw- mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
Pathogenesis & Immunity
verrucous lesions caused by human papillomavirus. (Reproduced with
permission from Wolff K, Johnson R. Fitzpatrick’s Color Atlas & Synopsis of Clinical Der-
Papillomaviruses infect squamous epithelial cells and
induce within those cells a characteristic perinuclear cyto-
Hill Companies, Inc.)
plasmic vacuole. These vacuolated cells, called koilocytes,
are the hallmark of infection by these viruses (Figure 38–2).
Most warts are benign and do not progress to malig-
[AIDS]) have more extensive warts, and women infected
nancy. However, HPV infection is associated with carci-
with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) have a very
noma of the uterine cervix and penis. The proteins encoded
high rate of carcinoma of the cervix.
by viral genes E6 and E7 interfere with the growth-inhibi-
tory activity of the proteins encoded by the p53 and RB
tumor suppressor genes and thereby contribute to onco-
Papillomas of various organs are the predominant finding.
genesis by these viruses. The E6 and E7 proteins of HPV-16 Clinical Findings
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com (condylomata acuminata) (Figure 38–4) are caused pri- mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
These papillomas are caused by specific HPV types. For
bind more strongly to p53 and RB proteins than the E6 and
example, skin and plantar warts (Figure 38–3) are caused
E7 proteins of HPV types not implicated in carcinomas—a
primarily by HPV-1 through HPV-4, whereas genital warts
finding that explains why HPV-16 causes carcinomas more
frequently than the other types of HPV.
marily by HPV-6 and HPV-11. HPV-6 and HPV-11 also
Both cell-mediated immunity and antibody are induced
cause respiratory tract papillomas, especially laryngeal
by viral infection and are involved in the spontaneous
papillomas, in young children.
regression of warts. Immunosuppressed patients (e.g.,
Carcinoma of the uterine cervix, the penis, and the anus,
patients with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome
as well as premalignant lesions called intraepithelial neo-
plasia, are associated with infection by HPV-16 and HPV-
18. The premalignant lesions are named for the organ
affected (e.g., cervical intraepithelial neoplasia [CIN],
penile intraepithelial neoplasia [PIN]). Occult premalig-
nant lesions of the cervix and penis can be revealed by
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com FIGURE 38–4 Papillomas (warts) on penis (condylomata acu- mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
FIGURE 38–2
Koilocytes. The black arrowhead points to a
koilocyte, seen here in a biopsy specimen of cervical intraepithelial
neoplasia caused by human papilloma virus. Koilocytes have a
small condensed nucleus and a large perinuclear cytoplasmis vacu-
minata)—note dry, raised verrucous lesions caused by human papil-
lomavirus. (Reproduced with permission from Wolff K, Johnson R. Fitzpatrick’s
ole. 400X magnification. (Reproduced with permission from Kemp, WL,
Color Atlas & Synopsis of Clinical Dermatology. 6th ed. New York: McGraw-Hill, 2009.
Burns, DK and Brown TG. Pathology: The Big picture. 1st ed. New York: McGraw-Hill,
Copyright © 2009 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.)
2008. Copyright © 2008 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.)
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com