Page 353 - Review of Medical Microbiology and Immunology ( PDFDrive )
P. 353
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com H A mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
41
P
C
E
T
R
Hepatitis Viruses
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com Hepatitis E Virus (HEV) mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com
CHAPTER C ONTENT S
Introduction
Hepatitis A Virus (HAV)
Hepatitis G Virus (HGV)
Self-Assessment Questions
Hepatitis B Virus (HBV)
Non-A, Non-B Hepatitis Viruses
Summaries of Organisms
Hepatitis C Virus (HCV)
Practice Questions: USMLE & Course Examinations
Hepatitis D Virus (HDV, Delta Virus)
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com fever virus, infect the liver but also infect other sites in the mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
INTRODUCTION
body and therefore are not exclusively hepatitis viruses.
Many viruses cause hepatitis. Of these, five medically
They are discussed elsewhere.
important viruses are commonly described as “hepatitis
viruses” because their main site of infection is the liver.
These five are hepatitis A virus (HAV), hepatitis B virus
HEPATITIS A VIRUS (HAV)
(HBV), hepatitis C virus (HCV), hepatitis D virus (HDV,
delta virus), and hepatitis E virus (HEV) (Tables 41–1 and
Disease
41–2). Other viruses, such as Epstein–Barr virus (the cause
of infectious mononucleosis), cytomegalovirus, and yellow
HAV causes hepatitis A.
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com continued presence indicates carrier state mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
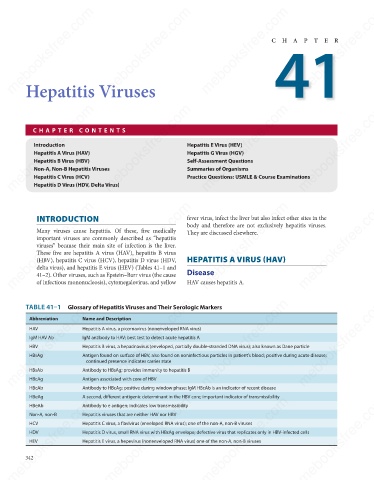
TABLE 41–1 Glossary of Hepatitis Viruses and Their Serologic Markers
Name and Description
Abbreviation
HAV
Hepatitis A virus, a picornavirus (nonenveloped RNA virus)
IgM antibody to HAV; best test to detect acute hepatitis A
IgM HAV Ab
HBV
Hepatitis B virus, a hepadnavirus (enveloped, partially double-stranded DNA virus); also known as Dane particle
HBsAg
Antigen found on surface of HBV, also found on noninfectious particles in patient’s blood; positive during acute disease;
HBsAb
Antibody to HBsAg; provides immunity to hepatitis B
HBcAg
Antigen associated with core of HBV
HBcAb
Antibody to HBcAg; positive during window phase; IgM HBcAb is an indicator of recent disease
A second, different antigenic determinant in the HBV core; important indicator of transmissibility
HBeAg
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com
HBeAb
Antibody to e antigen; indicates low transmissibility
Hepatitis viruses that are neither HAV nor HBV
Non-A, non-B
Hepatitis C virus, a flavivirus (enveloped RNA virus); one of the non-A, non-B viruses
HCV
Hepatitis D virus, small RNA virus with HBsAg envelope; defective virus that replicates only in HBV-infected cells
HDV
Hepatitis E virus, a hepevirus (nonenveloped RNA virus) one of the non-A, non-B viruses
HEV
342
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com