Page 356 - Review of Medical Microbiology and Immunology ( PDFDrive )
P. 356
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com animal reservoir. CHAPTER 41 Hepatitis Viruses 345 mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
Humans are the only natural hosts of HBV. There is no
Summary of Replicative Cycle
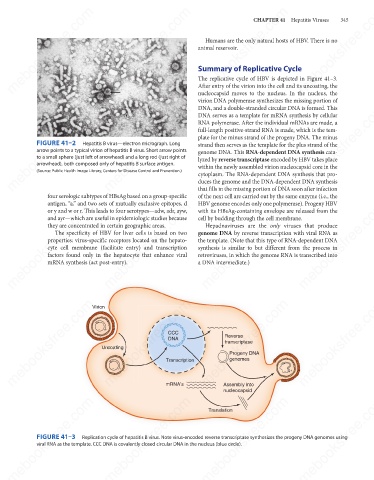
The replicative cycle of HBV is depicted in Figure 41–3.
After entry of the virion into the cell and its uncoating, the
nucleocapsid moves to the nucleus. In the nucleus, the
virion DNA polymerase synthesizes the missing portion of
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com full-length positive-strand RNA is made, which is the tem- mebooksfree.com
DNA, and a double-stranded circular DNA is formed. This
DNA serves as a template for mRNA synthesis by cellular
RNA polymerase. After the individual mRNAs are made, a
plate for the minus strand of the progeny DNA. The minus
FIGURE 41–2
Hepatitis B virus—electron micrograph. Long
strand then serves as the template for the plus strand of the
arrow points to a typical virion of hepatitis B virus. Short arrow points
genome DNA. This RNA-dependent DNA synthesis cata-
to a small sphere (just left of arrowhead) and a long rod (just right of
lyzed by reverse transcriptase encoded by HBV takes place
arrowhead), both composed only of hepatitis B surface antigen.
within the newly assembled virion nucleocapsid core in the
(Source: Public Health Image Library, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.)
duces the genome and the DNA-dependent DNA synthesis
that fills in the missing portion of DNA soon after infection
of the next cell are carried out by the same enzyme (i.e., the
four serologic subtypes of HBsAg based on a group-specific cytoplasm. The RNA-dependent DNA synthesis that pro-
HBV genome encodes only one polymerase). Progeny HBV
antigen, “a,” and two sets of mutually exclusive epitopes, d
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com genome DNA by reverse transcription with viral RNA as mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
with its HBsAg-containing envelope are released from the
or y and w or r. This leads to four serotypes—adw, adr, ayw,
cell by budding through the cell membrane.
and ayr—which are useful in epidemiologic studies because
Hepadnaviruses are the only viruses that produce
they are concentrated in certain geographic areas.
The specificity of HBV for liver cells is based on two
the template. (Note that this type of RNA-dependent DNA
properties: virus-specific receptors located on the hepato-
synthesis is similar to but different from the process in
cyte cell membrane (facilitate entry) and transcription
factors found only in the hepatocyte that enhance viral
retroviruses, in which the genome RNA is transcribed into
a DNA intermediate.)
mRNA synthesis (act post-entry).
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com Virion + mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com
–
CCC
Reverse
DNA
transcriptase
U Uncoating
Unc
Unc
Uncoating
Progeny DNA
genomes
Transcription
–
+
mRNA’s
Assembly into
nucleocapsid – +
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com
Translation
FIGURE 41–3
Replication cycle of hepatitis B virus. Note virus-encoded reverse transcriptase synthesizes the progeny DNA genomes using
viral RNA as the template. CCC DNA is covalently closed circular DNA in the nucleus (blue circle).
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com