Page 359 - Review of Medical Microbiology and Immunology ( PDFDrive )
P. 359
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com Prodrome, mebooksfree.com Prevention mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
PART IV Clinical Virology
348
Important diagnostic tests
Incubation
Convalescence
Prevention involves the use of either the vaccine or hyper-
period
acute disease
Early
Late
immune globulin or both.
Anti-
Anti-HBs
HBsAg
HBsAg
HBc
(anti-HBc)
(anti-HBc)
(1) The vaccine (e.g., Recombivax) contains HBsAg
A
1
0
2
5
4
6
3
vaccine is highly effective in preventing hepatitis B and has
few side effects. The seroconversion rate is approximately
95% in healthy adults. It is indicated for people who are
DNA polymerase Months after exposure 7 8 Anti-HBc produced in yeasts by recombinant DNA techniques. The
frequently exposed to blood or blood products, such as
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com HBeAg Window period Anti-HBe sions or dialysis, patients with frequent sexually transmitted mebooksfree.com
HBV virions
certain health care personnel (e.g., medical students, sur-
geons, and dentists), patients receiving multiple transfu-
HBsAg
disease, and abusers of illicit intravenous drugs. Travelers
Titer
who plan a long stay in areas of endemic infection, such as
Anti-HBs
many countries in Asia and Africa, should receive the vac-
cine. The U.S. Public Health Service recommends that all
newborns and adolescents receive the vaccine.
Level of
detection
At present, booster doses after the initial three-dose regi-
B
4
0
1
2
3
declined in immunized patients who are at high risk, such as
Months after exposure
dialysis patients, then a booster dose should be considered.
Elevated 5 6 7 8 men are not recommended. However, if antibody titers have
Widespread immunization with the HBV vaccine has
transaminases
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com both HBsAg and inactivated HAV provides protection mebooksfree.com
significantly reduced the incidence of hepatocellular carci-
Symptoms
C
noma in children. A vaccine called Twinrix that contains
against both hepatitis B and hepatitis A.
(2) Hepatitis B immune globulin (HBIG) contains a high
titer of HBsAb. It is used to provide immediate, passive pro-
tection to individuals known to be exposed to HBsAg-
positive blood (e.g., after an accidental needle-stick injury).
Titer
Precise recommendations for use of the vaccine and
HBIG are beyond the scope of this book. However, the
recommendation regarding one common concern of medi-
Total anti-HBc
HBsAg
cal students, the needle-stick injury from a patient with
HBsAg-positive blood, is that both the vaccine and HBIG
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com 4 5 mebooksfree.com newborn whose mother is HBsAg-positive. This regimen is mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
be given (at separate sites). This is true even if the patient’s
Level of
detection
blood is HBeAb positive.
Both the vaccine and HBIG should also be given to a
6
2
1
3
0
Years after exposure
Months after exposure
D
very effective in reducing the infection rate of newborns
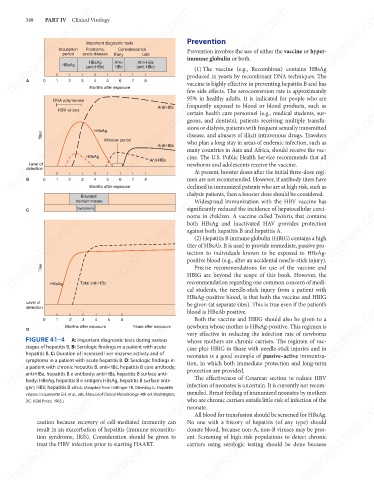
FIGURE 41–4
A: Important diagnostic tests during various
whose mothers are chronic carriers. The regimen of vac-
stages of hepatitis B. B: Serologic findings in a patient with acute
cine plus HBIG in those with needle-stick injuries and in
hepatitis B. C: Duration of increased liver enzyme activity and of
neonates is a good example of passive–active immuniza-
symptoms in a patient with acute hepatitis B. D: Serologic findings in
tion, in which both immediate protection and long-term
a patient with chronic hepatitis B. anti-HBc, hepatitis B core antibody;
anti-HBe, hepatitis B e antibody; anti-HBs, hepatitis B surface anti-
The effectiveness of Cesarean section to reduce HBV
body; HBeAg, hepatitis B e antigen; HBsAg, hepatitis B surface anti-
infection of neonates is uncertain. It is currently not recom-
gen; HBV, hepatitis B virus. (Adapted from Hollinger FB, Dienstag JL. Hepatitis
mended. Breast feeding of immunized neonates by mothers
viruses. In: Lennette EH, et al., eds. Manual of Clinical Microbiology. 4th ed. Washington, protection are provided.
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com No one with a history of hepatitis (of any type) should mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
who are chronic carriers entails little risk of infection of the
DC: ASM Press; 1985.)
neonate.
All blood for transfusion should be screened for HBsAg.
caution because recovery of cell-mediated immunity can
result in an exacerbation of hepatitis (immune reconstitu-
donate blood, because non-A, non-B viruses may be pres-
ent. Screening of high-risk populations to detect chronic
tion syndrome, IRIS). Consideration should be given to
carriers using serologic testing should be done because
treat the HBV infection prior to starting HAART.
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com