Page 483 - Review of Medical Microbiology and Immunology ( PDFDrive )
P. 483
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com Penetrate and develop mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com
PART VI Parasitology
472
Enterobiasis
(Enterobius vermicularis)
in mucosa
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com Ingested mebooksfree.com Human mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com
Adults in lumen
of cecum
Larvae hatch
in intestine
Adult female migrates
to perianal region
Embryonated egg
(Diagnostic stage)
(infective stage) Eggs on perianal folds
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com
External Environment
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mate, and produce thousands of fertilized eggs daily, mebooksfree.com
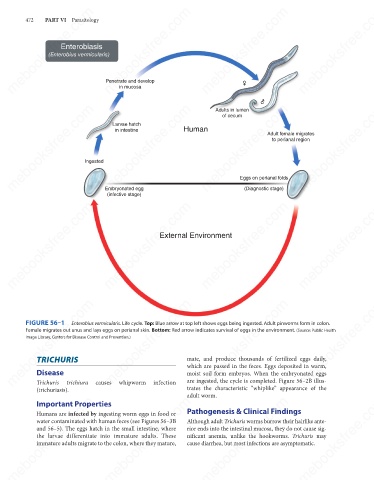
FIGURE 56–1
Enterobius vermicularis. Life cycle. Top: Blue arrow at top left shows eggs being ingested. Adult pinworms form in colon.
Female migrates out anus and lays eggs on perianal skin. Bottom: Red arrow indicates survival of eggs in the environment. (Source: Public Health
Image Library, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.)
TRICHURIS
which are passed in the feces. Eggs deposited in warm,
Disease
are ingested, the cycle is completed. Figure 56–2B illus-
Trichuris
trates the characteristic “whiplike” appearance of the
(trichuriasis). trichiura causes whipworm infection moist soil form embryos. When the embryonated eggs
adult worm.
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com Although adult Trichuris worms burrow their hairlike ante- mebooksfree.com
Important Properties
Pathogenesis & Clinical Findings
Humans are infected by ingesting worm eggs in food or
water contaminated with human feces (see Figures 56–3B
and 56–5). The eggs hatch in the small intestine, where
rior ends into the intestinal mucosa, they do not cause sig-
the larvae differentiate into immature adults. These
nificant anemia, unlike the hookworms. Trichuris may
cause diarrhea, but most infections are asymptomatic.
immature adults migrate to the colon, where they mature,
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com