Page 576 - Review of Medical Microbiology and Immunology ( PDFDrive )
P. 576
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com (A) Allergen binds to IgE on the surface of B cells and IL-4 is mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
565
CHAPTER 65 Hypersensitivity (Allergy)
skin tests with various allergens. A wheal-and-flare reaction is
seen on the patient’s back at the site where several pollens were
injected. What is the most likely sequence of events that produced
the wheal-and-flare reaction?
released.
(B) Allergen binds to IgE on the surface of mast cells and histamine
is released.
(C) Allergen binds to IgE in the plasma, which activates comple-
ment to produce C3b.
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com (A) Cytotoxic T cells kill target cells at the site. mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com
(D) Allergen binds to IgE in the plasma, and the allergen-IgE com-
plex binds to the surface of macrophages and IL-1 is released.
2. One important test to determine whether your patient has been
exposed to M. tuberculosis, the organism that causes tuberculosis,
is to do a PPD skin test. In this test, PPD extracted from the organ-
ism is injected intradermally. Of the following, which one is most
likely to occur at the site of a positive PPD?
(B) Macrophages and CD4-positive T cells infiltrate the site.
(C) Histamine and leukotrienes are liberated from mast cells at
the site.
(D) Immune complexes consisting of PPD and IgG are deposited at
the site.
3. Your patient is a 77-year-old man with enterococcal endocardi-
tis who was treated with penicillin G and gentamicin. Five days
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com (A) One of the drugs formed immune complexes with IgG. mebooksfree.com
later, fever and a diffuse maculopapular rash developed. There is
no urticaria, hypotension, or respiratory compromise. Urinalysis
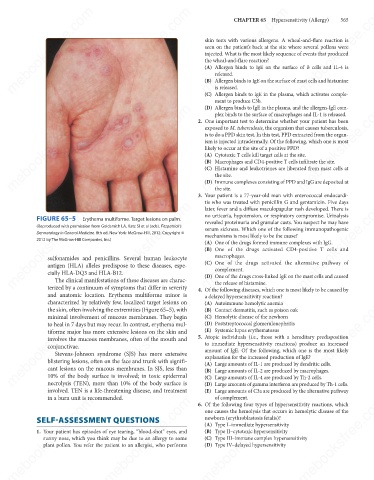
FIGURE 65–5
Erythema multiforme. Target lesions on palm.
revealed proteinuria and granular casts. You suspect he may have
(Reproduced with permission from Goldsmith LA, Katz SI et al (eds). Fitzpatrick’s
serum sickness. Which one of the following immunopathogenic
Dermatology in General Medicine. 8th ed. New York: McGraw-Hill, 2012. Copyright ©
mechanisms is most likely to be the cause?
2012 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.)
(B) One of the drugs activated CD4-positive T cells and
macrophages.
sulfonamides and penicillins. Several human leukocyte
(C) One of the drugs activated the alternative pathway of
antigen (HLA) alleles predispose to these diseases, espe-
complement.
cially HLA-DQ3 and HLA-B12.
(D) One of the drugs cross-linked IgE on the mast cells and caused
The clinical manifestations of these diseases are charac-
the release of histamine.
terized by a continuum of symptoms that differ in severity
and anatomic location. Erythema multiforme minor is 4. Of the following diseases, which one is most likely to be caused by
a delayed hypersensitivity reaction?
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com 5. Atopic individuals (i.e., those with a hereditary predisposition mebooksfree.com
characterized by relatively few, localized target lesions on
(A) Autoimmune hemolytic anemia
the skin, often involving the extremities (Figure 65–5), with
(B) Contact dermatitis, such as poison oak
minimal involvement of mucous membranes. They begin
(C) Hemolytic disease of the newborn
(D) Poststreptococcal glomerulonephritis
to heal in 7 days but may recur. In contrast, erythema mul-
(E) Systemic lupus erythematosus
tiforme major has more extensive lesions on the skin and
involves the mucous membranes, often of the mouth and
to immediate hypersensitivity reactions) produce an increased
conjunctivae.
amount of IgE. Of the following, which one is the most likely
Stevens-Johnson syndrome (SJS) has more extensive
explanation for the increased production of IgE?
blistering lesions, often on the face and trunk with signifi-
(A) Large amounts of IL-1 are produced by dendritic cells.
cant lesions on the mucous membranes. In SJS, less than
(B) Large amounts of IL-2 are produced by macrophages.
10% of the body surface is involved; in toxic epidermal
(C) Large amounts of IL-4 are produced by Th-2 cells.
necrolysis (TEN), more than 10% of the body surface is
(D) Large amounts of gamma interferon are produced by Th-1 cells.
involved. TEN is a life-threatening disease, and treatment 6. Of the following four types of hypersensitivity reactions, which
(E) Large amounts of C3a are produced by the alternative pathway
in a burn unit is recommended.
of complement.
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com (A) Type I–immediate hypersensitivity mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
one causes the hemolysis that occurs in hemolytic disease of the
SELF-ASSESSMENT QUESTIONS
newborn (erythroblastosis fetalis)?
1. Your patient has episodes of eye tearing, “blood-shot” eyes, and
(B) Type II–cytotoxic hypersensitivity
runny nose, which you think may be due to an allergy to some
(C) Type III–immune complex hypersensitivity
(D) Type IV–delayed hypersensitivity
plant pollen. You refer the patient to an allergist, who performs
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com