Page 65 - Review of Medical Microbiology and Immunology ( PDFDrive )
P. 65
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com structure called an inflammasome. The importance of the mebooksfree.com
PART I Basic Bacteriology
54
the normal flora is appreciated in the occasional case when
antimicrobial therapy suppresses these beneficial organisms,
inflammatory response in limiting infection is emphasized
thereby allowing organisms such as Clostridium difficile and
by the ability of anti-inflammatory agents such as corticoste-
roids to lower resistance to infection.
Candida albicans to cause diseases such as pseudomembra-
nous colitis and vaginitis, respectively.
Certain proteins, known collectively as the acute-phase
response, are also produced early in inflammation, mainly
by the liver. The best known of these are C-reactive protein
Inflammatory Response &
and mannose-binding protein, which bind to the surface
Phagocytosis
of bacteria and enhance the activation of the alternative
The presence of foreign bodies, such as bacteria within
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com pathway of complement (see Chapter 58). C-reactive pro- mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
the body, provokes a protective inflammatory response
tein was named for its ability to bind with a carbohydrate in
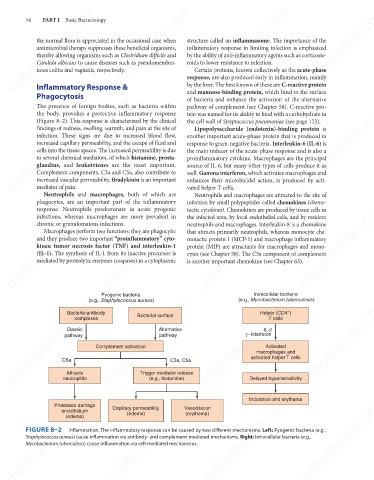
(Figure 8–2). This response is characterized by the clinical
the cell wall of Streptococcus pneumoniae (see page 123).
findings of redness, swelling, warmth, and pain at the site of
Lipopolysaccharide (endotoxin)-binding protein is
infection. These signs are due to increased blood flow,
another important acute-phase protein that is produced in
increased capillary permeability, and the escape of fluid and
response to gram-negative bacteria. Interleukin-6 (IL-6) is
cells into the tissue spaces. The increased permeability is due
the main inducer of the acute-phase response and is also a
to several chemical mediators, of which histamine, prosta-
proinflammatory cytokine. Macrophages are the principal
glandins, and leukotrienes are the most important.
source of IL-6, but many other types of cells produce it as
Complement components, C3a and C5a, also contribute to
increased vascular permeability. Bradykinin is an important
enhances their microbicidal action, is produced by acti-
mediator of pain.
vated helper T cells.
Neutrophils and macrophages, both of which are well. Gamma interferon, which activates macrophages and
Neutrophils and macrophages are attracted to the site of
phagocytes, are an important part of the inflammatory
infection by small polypeptides called chemokines (chemo-
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com neutrophils and macrophages. Interleukin-8 is a chemokine mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
response. Neutrophils predominate in acute pyogenic
tactic cytokines). Chemokines are produced by tissue cells in
infections, whereas macrophages are more prevalent in
the infected area, by local endothelial cells, and by resident
chronic or granulomatous infections.
Macrophages perform two functions: they are phagocytic
that attracts primarily neutrophils, whereas monocyte che-
and they produce two important “proinflammatory” cyto-
motactic protein 1 (MCP-1) and macrophage inflammatory
kines: tumor necrosis factor (TNF) and interleukin-1
protein (MIP) are attractants for macrophages and mono-
(IL-1). The synthesis of IL-1 from its inactive precursor is
cytes (see Chapter 58). The C5a component of complement
mediated by proteolytic enzymes (caspases) in a cytoplasmic
is another important chemokine (see Chapter 63).
Intracellular bacteria
Pyogenic bacteria (e.g., Mycobacterium tuberculosis)
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com Complement activation (e.g., histamine) mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com
(e.g., Staphylococcus aureus)
mebooksfree.com
+
Helper (CD4 )
Bacteria-antibody
Bacterial surface
T cells
complexes
Alternative
Classic
IL-2
γ−Interferon
pathway
pathway
Activated
macrophages and
activated helper T cells
C5a
C3a, C5a
Trigger mediator release
Attracts
Delayed hypersensitivity
neutrophils
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com Vasodilation Induration and erythema mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
Proteases damage
Capillary permeability
endothelium
(erythema)
(edema)
(edema)
FIGURE 8–2
Inflammation. The inflammatory response can be caused by two different mechanisms. Left: Pyogenic bacteria (e.g.,
Staphylococcus aureus) cause inflammation via antibody- and complement-mediated mechanisms. Right: Intracellular bacteria (e.g.,
Mycobacterium tuberculosis) cause inflammation via cell-mediated mechanisms.
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com