Page 56 - PRE-U STPM BIOLOGY TERM 1
P. 56
Biology Term 1 STPM Chapter 2 Structure of Cells and Organelles
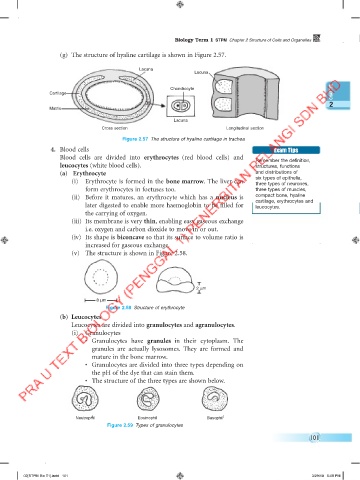
(g) The structure of hyaline cartilage is shown in Figure 2.57.
Lacuna
Lacuna
Chondrocyte
Cartilage
2
Matrix
Lacuna
Cross section Longitudinal section
Figure 2.57 The structure of hyaline cartilage in trachea
4. Blood cells Exam Tips
Blood cells are divided into erythrocytes (red blood cells) and Remember the definition,
leucocytes (white blood cells). structures, functions
(a) Erythrocyte and distributions of
(i) Erythrocyte is formed in the bone marrow. The liver can six types of epithelia,
three types of neurones,
form erythrocytes in foetuses too. three types of muscles,
(ii) Before it matures, an erythrocyte which has a nucleus is compact bone, hyaline
later digested to enable more haemoglobin to be filled for cartilage, erythrocytes and
leucocytes.
the carrying of oxygen.
(iii) Its membrane is very thin, enabling easy gaseous exchange
i.e. oxygen and carbon dioxide to move in or out.
(iv) Its shape is biconcave so that its surface to volume ratio is
increased for gaseous exchange.
(v) The structure is shown in Figure 2.58.
2 μm
8 μm
Figure 2.58 Structure of erythrocyte
(b) Leucocytes
Leucocytes are divided into granulocytes and agranulocytes.
(i) Granulocytes
• Granulocytes have granules in their cytoplasm. The
granules are actually lysosomes. They are formed and
mature in the bone marrow.
• Granulocytes are divided into three types depending on
the pH of the dye that can stain them.
• The structure of the three types are shown below.
Neutrophill Eosinophil Basophill
Basophil
Neutrophil
Figure 2.59 Types of granulocytes
101
02[STPM Bio T1].indd 101 3/29/18 5:08 PM