Page 55 - PRE-U STPM BIOLOGY TERM 1
P. 55
Biology Term 1 STPM Chapter 2 Structure of Cells and Organelles
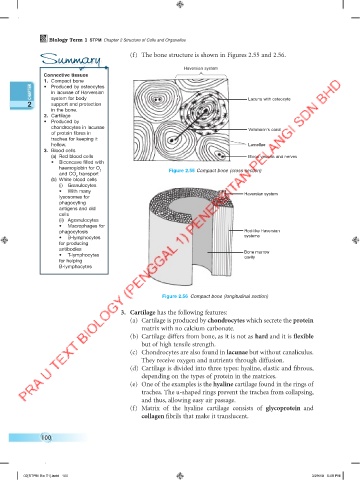
Summary (f) The bone structure is shown in Figures 2.55 and 2.56.
Haversian system
Connective tissues
1. Compact bone
• Produced by osteocytes
in lacunae of Harversian
system for body Lacuna with osteocyte
2 support and protection
in the bone.
2. Cartilage
• Produced by
chondrocytes in lacunae Volkmann’s canal
of protein fibres in
trachea for keeping it
hollow. Lamellae
3. Blood cells
(a) Red blood cells Blood vessels and nerves
• Biconcave filled with
haemoglobin for O Figure 2.55 Compact bone (cross section)
2
and CO transport
2
(b) White blood cells
(i) Granulocytes
• With many Haversian system
lysosomes for
phagocyting
antigens and old
cells
(ii) Agranulocytes
• Macrophages for
phagocytosis Rod-like Haversian
• B-lymphocytes systems
for producing
antibodies
• T-lymphocytes Bone marrow
cavity
for helping
B-lymphocytes
Figure 2.56 Compact bone (longitudinal section)
3. Cartilage has the following features:
(a) Cartilage is produced by chondrocytes which secrete the protein
matrix with no calcium carbonate.
(b) Cartilage differs from bone, as it is not as hard and it is flexible
but of high tensile strength.
(c) Chondrocytes are also found in lacunae but without canaliculus.
They receive oxygen and nutrients through diffusion.
(d) Cartilage is divided into three types: hyaline, elastic and fibrous,
depending on the types of protein in the matrices.
(e) One of the examples is the hyaline cartilage found in the rings of
trachea. The u-shaped rings prevent the trachea from collapsing,
and thus, allowing easy air passage.
(f) Matrix of the hyaline cartilage consists of glycoprotein and
collagen fibrils that make it translucent.
100
02[STPM Bio T1].indd 100 3/29/18 5:08 PM