Page 58 - PRE-U STPM CHEMISTRY TERM 1
P. 58
Chemistry Term 1 STPM
pH Since the ionic quotient is larger than the
solubility product (2.00 × 10 ). Precipitation
–13
will occur.
6.0
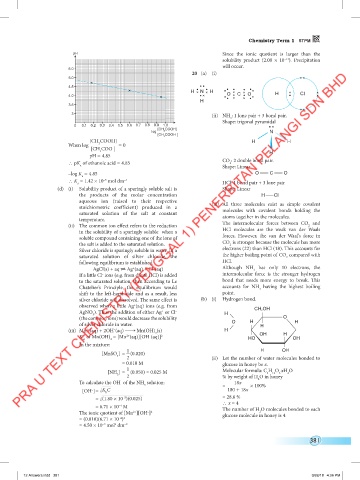
20 (a) (i)
5.0
4.5
H N H H N H H N H H H H
4.0 O C O O C O O C O CI CI CI
H H H
3.5
3
(ii) NH : 1 lone pair + 3 bond pair.
3
Shape: trigonal pyramidal
0 0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4 0.5 0.6 0.7 0.8 0.9 1.0
log [CH 3 COOH] N
[CH 3 COOH – ]
[CH COOH] H H
When log 3 = 0
–
[CH COO ]
3 H
pH = 4.85 CO : 2 double bond pair.
∴ pK of ethanoic acid = 4.85 Shape: Linear
2
a
–log K = 4.85 O C O
a
∴ K = 1.42 × 10 mol dm –3 HCl: 1 bond pair + 3 lone pair
–5
a
(d) (i) Solubility product of a sparingly soluble salt is Shape: Linear
the products of the molar concentration H CI
aqueous ion (raised to their respective
stoichiometric coefficient) produced in a (iii) All three molecules exist as simple covalent
saturated solution of the salt at constant molecules with covalent bonds holding the
temperature. atoms together in the molecules.
(ii) The common ion effect refers to the reduction The intermolecular forces between CO and
2
in the solubility of a sparingly soluble when a HCl molecules are the weak van der Waals
soluble compound containing one of the ions of forces. However, the van der Waal’s force in
the salt is added to the saturated solution. CO is stronger because the molecule has more
2
Silver chloride is sparingly soluble in water. In a electrons (22) than HCl (18). This accounts for
saturated solution of silver chloride, the the higher boiling point of CO compared with
2
following equilibrium is established. HCl.
AgCl(s) + aq Ag (aq) + Cl (aq) Although NH has only 10 electrons, the
+
–
3
If a little Cl ions (e.g. from dilute HCl) is added intermolecular force is the stronger hydrogen
–
to the saturated solution, then according to Le bond that needs more energy to break. This
Chatelier’s Principle, the equilibrium would accounts for NH having the highest boiling
3
shift to the left-hand side and as a result, less point.
silver chloride will dissolved. The same effect is (b) (i) Hydrogen bond.
observed when a little Ag (aq) ions (e.g. from
+
AgNO ). Thus the addition of either Ag or Cl – H CH OH
+
2
3
(the common ions) would decrease the solubility O
of silver chloride in water. O H H H
(iii) Mn (aq) + 2OH (aq) 9: Mn(OH) (s) H
–
2+
2
K of Mn(OH) = [Mn (aq)][OH (aq)] 2 OH H
2+
–
sp 2 HO OH
In the mixture:
1 H OH
[MnSO ] = (0.020)
4
2 (ii) Let the number of water molecules bonded to
= 0.010 M glucose in honey be x.
1 Molecular formula: C H O xH O
[NH ] = (0.050) = 0.025 M 6 12 6 2
3
2 % by weight of H O in honey
2
To calculate the OH of the NH solution: 18x
–
3 = × 100%
[OH ] = K C 180 + 18x
–
b
= (1.80 × 10 )(0.025) = 28.6 %
–5
= 6.71 × 10 M ∴ x = 4
–4
The number of H O molecules bonded to each
The ionic quotient of [Mn ][OH ] glucose molecule in honey is 4.
2
2+
– 2
= (0.010)(6.71 × 10 )
–4 2
= 4.50 × 10 mol dm –9
3
–9
381
12 Answers.indd 381 3/26/18 4:06 PM