Page 22 - Focus TG4 KSSM (Physics) Terbitan Penerbitan Pelangi Sdn Bhd
P. 22
Physics Form 4 Chapter 2 Force and Motion I
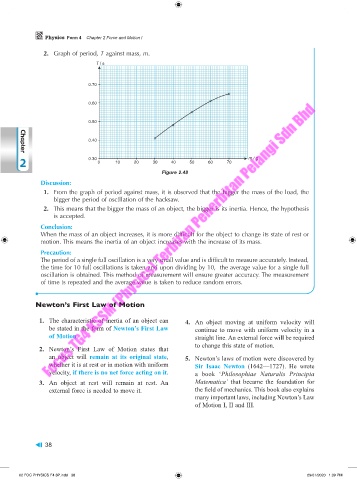
2. Graph of period, T against mass, m.
T / s
0.70
0.60
0.50
0.40
Chapter
2 0.30 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 m / g
Figure 2.48
Discussion:
1. From the graph of period against mass, it is observed that the bigger the mass of the load, the
bigger the period of oscillation of the hacksaw.
2. This means that the bigger the mass of an object, the bigger is its inertia. Hence, the hypothesis
is accepted.
Conclusion:
When the mass of an object increases, it is more difficult for the object to change its state of rest or
motion. This means the inertia of an object increases with the increase of its mass.
Precaution:
The period of a single full oscillation is a very small value and is difficult to measure accurately. Instead,
the time for 10 full oscillations is taken and upon dividing by 10, the average value for a single full
oscillation is obtained. This method of measurement will ensure greater accuracy. The measurement
of time is repeated and the average value is taken to reduce random errors.
Newton’s First Law of Motion
1. The characteristic of inertia of an object can 4. An object moving at uniform velocity will
be stated in the form of Newton’s First Law continue to move with uniform velocity in a
of Motion. straight line. An external force will be required
to change this state of motion.
2. Newton’s First Law of Motion states that
an object will remain at its original state, 5. Newton’s laws of motion were discovered by
whether it is at rest or in motion with uniform Sir Isaac Newton (1642—1727). He wrote
velocity, if there is no net force acting on it. a book ‘Philosophiae Naturalis Principia
3. An object at rest will remain at rest. An Matematica’ that became the foundation for
external force is needed to move it. the field of mechanics. This book also explains
many important laws, including Newton’s Law
of Motion I, II and III.
38
02 FOC PHYSICS F4 3P.indd 38 29/01/2020 1:39 PM