Page 34 - Focus TG4 KSSM (Physics) Terbitan Penerbitan Pelangi Sdn Bhd
P. 34
Physics Form 4 Chapter 2 Force and Motion I
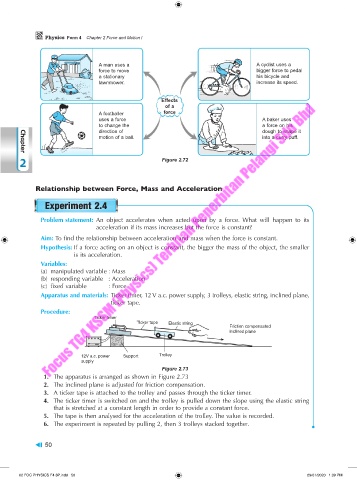
A man uses a A cyclist uses a
force to move bigger force to pedal
a stationary his bicycle and
lawnmower. increase its speed.
Effects
of a
A footballer force
uses a force A baker uses
to change the a force on his
direction of dough to shape it
motion of a ball. into a curry puff.
Chapter
2 Figure 2.72
Relationship between Force, Mass and Acceleration
Eksperimen 2.1
Experiment 2.4
Eksperimen 2.1
Problem statement: An object accelerates when acted upon by a force. What will happen to its
acceleration if its mass increases but the force is constant?
Aim: To find the relationship between acceleration and mass when the force is constant.
Hypothesis: If a force acting on an object is constant, the bigger the mass of the object, the smaller
is its acceleration.
Variables:
(a) manipulated variable : Mass
(b) responding variable : Acceleration
(c) fixed variable : Force
Apparatus and materials: Ticker timer, 12 V a.c. power supply, 3 trolleys, elastic string, inclined plane,
ticker tape.
Procedure:
Ticker timer
Ticker tape Elastic string
Friction compensated
inclined plane
12V a.c. power Support Trolley
supply
Figure 2.73
1. The apparatus is arranged as shown in Figure 2.73
2. The inclined plane is adjusted for friction compensation.
3. A ticker tape is attached to the trolley and passes through the ticker timer.
4. The ticker timer is switched on and the trolley is pulled down the slope using the elastic string
that is stretched at a constant length in order to provide a constant force.
5. The tape is then analysed for the acceleration of the trolley. The value is recorded.
6. The experiment is repeated by pulling 2, then 3 trolleys stacked together.
50
02 FOC PHYSICS F4 3P.indd 50 29/01/2020 1:39 PM