Page 4 - Focus TG4 KSSM (Physics) Terbitan Penerbitan Pelangi Sdn Bhd
P. 4
Physics Form 4 Chapter 2 Force and Motion I
2. Non-linear motion is motion that is not in a
2.1 Linear Motion straight line.
3. When analysing linear and non-linear motion,
My motion is a distance, displacement, speed, velocity,
linear motion My motion is a
non-linear motion Start acceleration and deceleration are commonly
Start End End Not a straight line encountered physical quantities.
A straight line SPM Tips
Figure 2.1
Speed (scalar quantity)—magnitude only
1. Linear motion is a motion in a straight line. Velocity (vector quantity)—magnitude and direction
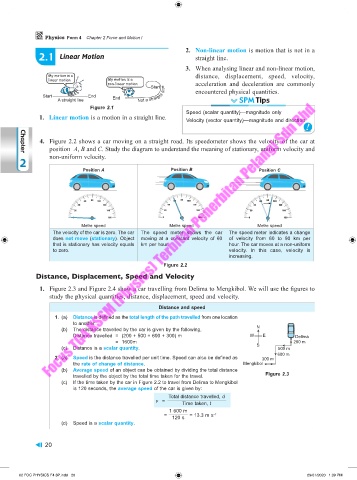
4. Figure 2.2 shows a car moving on a straight road. Its speedometer shows the velocity of the car at
position A, B and C. Study the diagram to understand the meaning of stationary, uniform velocity and
non-uniform velocity.
Chapter
2
Kedudukan A Kedudukan B Kedudukan C
Position B
Position A
Position C
Metre speed Metre speed Metre speed
The velocity of the car is zero. The car The speed meter shows the car The speed meter indicates a change
does not move (stationary). Object moving at a constant velocity of 60 of velocity from 60 to 90 km per
that is stationary has velocity equals km per hour. hour. The car moves at a non-uniform
to zero. velocity. In this case, velocity is
increasing.
Figure 2.2
Distance, Displacement, Speed and Velocity
1. Figure 2.3 and Figure 2.4 show a car travelling from Delima to Mengkibol. We will use the figures to
study the physical quantities, distance, displacement, speed and velocity.
Distance and speed
1. (a) Distance is defined as the total length of the path travelled from one location
to another.
(b) The distance travelled by the car is given by the following, N
Distance travelled = (200 + 500 + 600 + 300) m W E Delima
= 1600m 200 m
(c) Distance is a scalar quantity. S 500 m
600 m
2. (a) Speed is the distance travelled per unit time. Speed can also be defined as 300 m
the rate of change of distance. Mengkibol
(b) Average speed of an object can be obtained by dividing the total distance
travelled by the object by the total time taken for the travel. Figure 2.3
(c) If the time taken by the car in Figure 2.2 to travel from Delima to Mengkibol
is 120 seconds, the average speed of the car is given by:
Total distance travelled, d
v = Time taken, t
1 600 m
= 120 s = 13.3 m s –1
(d) Speed is a scalar quantity.
20
02 FOC PHYSICS F4 3P.indd 20 29/01/2020 1:39 PM