Page 8 - Ranger SPM 2022 - Science
P. 8
Science SPM Chapter 1 Safety Measures in the Laboratory
1.2 Disposal of Waste
Waste that Can be Disposed of into Sinks and Waste that Cannot be Disposed
Penerbitan Pelangi Sdn Bhd. All Rights Reserved.
of into Sinks
1. There are two types of laboratory waste:
(a) substances that can be disposed of into sinks
(b) substances that cannot be disposed of into sinks
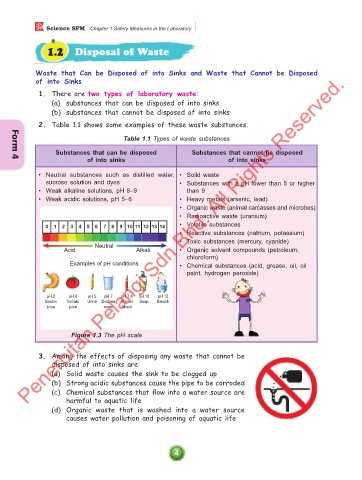
2. Table 1.1 shows some examples of these waste substances.
Table 1.1 Types of waste substances
Substances that can be disposed Substances that cannot be disposed
of into sinks of into sinks
Form 4
• Neutral substances such as distilled water, • Solid waste
sucrose solution and dyes • Substances with a pH lower than 5 or higher
• Weak alkaline solutions, pH 8–9 than 9
• Weak acidic solutions, pH 5–6 • Heavy metals (arsenic, lead)
• Organic waste (animal carcasses and microbes)
• Radioactive waste (uranium)
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 • Volatile substances
• Reactive substances (natrium, potassium)
• Toxic substances (mercury, cyanide)
Neutral
Acid Alkali • Organic solvent compounds (petroleum,
chloroform)
Examples of pH conditions • Chemical substances (acid, grease, oil, oil
paint, hydrogen peroxide)
pH 2 pH 4 pH 5 pH 7 pH 7.4 pH 10 pH 12
Gastric Tomato Urine Distilled Human Soap Bleach
juice juice water blood
Figure 1.3 The pH scale
3. Among the effects of disposing any waste that cannot be
disposed of into sinks are:
(a) Solid waste causes the sink to be clogged up
(b) Strong acidic substances cause the pipe to be corroded
(c) Chemical substances that flow into a water source are
harmful to aquatic life
(d) Organic waste that is washed into a water source
causes water pollution and poisoning of aquatic life
4
F4 Chapter 1.indd 4 3/21/22 3:02 PM