Page 26 - Ranger SPM 2022 Biology
P. 26
Biology SPM Chapter 2 Leaf Structure and Function
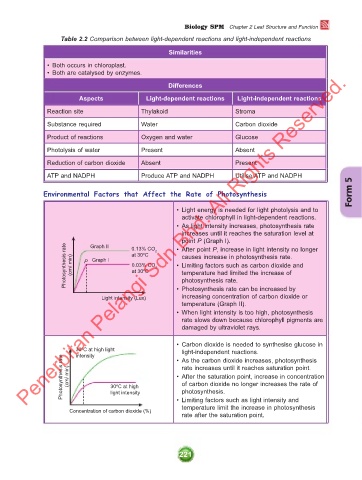
Table 2.2 Comparison between light-dependent reactions and light-independent reactions
Similarities
• Both occurs in chloroplast.
• Both are catalysed by enzymes.
Penerbitan Pelangi Sdn Bhd. All Rights Reserved.
Differences
Aspects Light-dependent reactions Light-independent reactions
Reaction site Thylakoid Stroma
Substance required Water Carbon dioxide
Product of reactions Oxygen and water Glucose
Photolysis of water Present Absent
Reduction of carbon dioxide Absent Present
ATP and NADPH Produce ATP and NADPH Utilise ATP and NADPH
Form 5
Environmental Factors that Affect the Rate of Photosynthesis
• Light energy is needed for light photolysis and to
activate chlorophyll in light-dependent reactions.
• As light intensity increases, photosynthesis rate
increases until it reaches the saturation level at
point P (Graph I).
Photosynthesis rate (cm/ min) P Graph I at 30ºC 2 • Limiting factors such as carbon dioxide and
Graph II
• After point P, increase in light intensity no longer
0.13% CO
2
causes increase in photosynthesis rate.
0.03% CO
at 30ºC
temperature had limited the increase of
photosynthesis rate.
increasing concentration of carbon dioxide or
Light intensity (Lux) • Photosynthesis rate can be increased by
temperature (Graph II).
• When light intensity is too high, photosynthesis
rate slows down because chlorophyll pigments are
damaged by ultraviolet rays.
• Carbon dioxide is needed to synthesise glucose in
30ºC at high light • As the carbon dioxide increases, photosynthesis
light-independent reactions.
intensity
Photosynthesis rate (cm/ min) 30ºC at high • After the saturation point, increase in concentration
rate increases until it reaches saturation point.
of carbon dioxide no longer increases the rate of
photosynthesis.
light intensity
• Limiting factors such as light intensity and
temperature limit the increase in photosynthesis
Concentration of carbon dioxide (%)
rate after the saturation point.
221
F5 Chapter 2.indd 221 3/29/22 4:35 PM