Page 22 - Ranger SPM 2022 Biology
P. 22
Biology SPM Chapter 2 Leaf Structure and Function
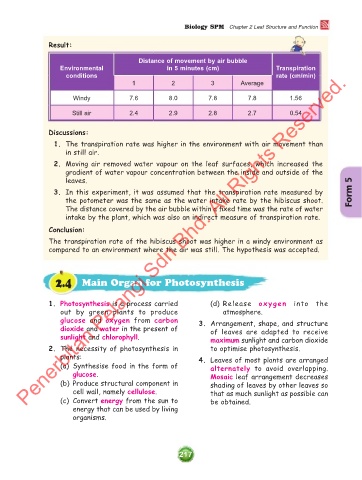
Result:
Distance of movement by air bubble
Environmental in 5 minutes (cm) Transpiration
Penerbitan Pelangi Sdn Bhd. All Rights Reserved.
conditions rate (cm/min)
1 2 3 Average
Windy 7.6 8.0 7.8 7.8 1.56
Still air 2.4 2.9 2.8 2.7 0.54
Discussions:
1. The transpiration rate was higher in the environment with air movement than
in still air.
2. Moving air removed water vapour on the leaf surfaces, which increased the
gradient of water vapour concentration between the inside and outside of the
leaves.
3. In this experiment, it was assumed that the transpiration rate measured by Form 5
the potometer was the same as the water intake rate by the hibiscus shoot.
The distance covered by the air bubble within a fixed time was the rate of water
intake by the plant, which was also an indirect measure of transpiration rate.
Conclusion:
The transpiration rate of the hibiscus shoot was higher in a windy environment as
compared to an environment where the air was still. The hypothesis was accepted.
2.4 Main Organ for Photosynthesis
1. Photosynthesis is a process carried (d) Release oxygen into the
out by green plants to produce atmosphere.
glucose and oxygen from carbon 3. Arrangement, shape, and structure
dioxide and water in the present of of leaves are adapted to receive
sunlight and chlorophyll. maximum sunlight and carbon dioxide
2. The necessity of photosynthesis in to optimise photosynthesis.
plants: 4. Leaves of most plants are arranged
(a) Synthesise food in the form of alternately to avoid overlapping.
glucose. Mosaic leaf arrangement decreases
(b) Produce structural component in shading of leaves by other leaves so
cell wall, namely cellulose. that as much sunlight as possible can
(c) Convert energy from the sun to be obtained.
energy that can be used by living
organisms.
217
F5 Chapter 2.indd 217 3/29/22 4:35 PM