Page 12 - Q & A STPM 2022 Biology
P. 12
Biology STPM Chapter 3 Membrane Structure and Transport
Question 10
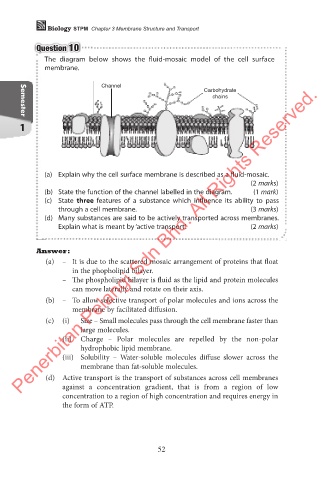
The diagram below shows the fluid-mosaic model of the cell surface
membrane.
Penerbitan Pelangi Sdn Bhd. All Rights Reserved.
Channel
Carbohydrate
chains
Semester
1
(a) Explain why the cell surface membrane is described as a fluid-mosaic.
(2 marks)
(b) State the function of the channel labelled in the diagram. (1 mark)
(c) State three features of a substance which influence its ability to pass
through a cell membrane. (3 marks)
(d) Many substances are said to be actively transported across membranes.
Explain what is meant by ‘active transport’. (2 marks)
Answer :
(a) – It is due to the scattered mosaic arrangement of proteins that float
in the phopholipid bilayer.
– The phospholipid bilayer is fluid as the lipid and protein molecules
can move laterally and rotate on their axis.
(b) – To allow selective transport of polar molecules and ions across the
membrane by facilitated diffusion.
(c) (i) Size – Small molecules pass through the cell membrane faster than
large molecules.
(ii) Charge – Polar molecules are repelled by the non-polar
hydrophobic lipid membrane.
(iii) Solubility – Water-soluble molecules diffuse slower across the
membrane than fat-soluble molecules.
(d) Active transport is the transport of substances across cell membranes
against a concentration gradient, that is from a region of low
concentration to a region of high concentration and requires energy in
the form of ATP.
52
Chapter 3.indd 52 11/2/21 9:21 AM