Page 6 - Focus SPM KSSM F4 2020 - Chemistry
P. 6
Chemistry Form 4 Chapter 3 The Mole Concept, Chemical Formula and Equation
3.1 Relative Atomic Mass and Relative Molecular Mass
Relative Atomic Mass, RAM
1. An atom has a very small mass and thus, is difficult to measure. Therefore, chemists compare the mass
of an atom with that of a standard atom.
2. The mass of an atom compared to a standard atom is called relative atomic mass. Relative atomic
mass has no unit as it is just a comparison value.
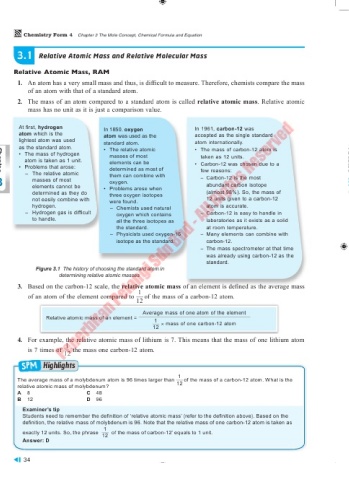
At first, hydrogen In 1850, oxygen In 1961, carbon-12 was
atom which is the atom was used as the accepted as the single standard
lightest atom was used standard atom. atom internationally.
as the standard atom. • The relative atomic • The mass of carbon-12 atom is
• The mass of hydrogen masses of most taken as 12 units.
atom is taken as 1 unit. elements can be
• Problems that arose: determined as most of • Carbon-12 was chosen due to a
– The relative atomic them can combine with few reasons:
Chapter
3 masses of most oxygen. – Carbon-12 is the most
abundant carbon isotope
elements cannot be
determined as they do • Problems arose when (almost 98%). So, the mass of
three oxygen isotopes
not easily combine with were found. 12 units given to a carbon-12
hydrogen. – Chemists used natural atom is accurate.
– Hydrogen gas is difficult oxygen which contains – Carbon-12 is easy to handle in
to handle. all the three isotopes as laboratories as it exists as a solid
the standard. at room temperature.
– Physicists used oxygen-16 – Many elements can combine with
isotope as the standard. carbon-12.
– The mass spectrometer at that time
was already using carbon-12 as the
standard.
Figure 3.1 The history of choosing the standard atom in
determining relative atomic masses
3. Based on the carbon-12 scale, the relative atomic mass of an element is defined as the average mass
of an atom of the element compared to 1 of the mass of a carbon-12 atom.
12
Average mass of one atom of the element
Relative atomic mass of an element = 1
12 × mass of one carbon-12 atom
4. For example, the relative atomic mass of lithium is 7. This means that the mass of one lithium atom
1
is 7 times of 12 the mass one carbon-12 atom.
SPM Highlights
1
The average mass of a molybdenum atom is 96 times larger than 12 of the mass of a carbon-12 atom. What is the
relative atomic mass of molybdenum?
A 8 C 48
B 12 D 96
Examiner’s tip
Students need to remember the definition of ‘relative atomic mass’ (refer to the definition above). Based on the
definition, the relative mass of molybdenum is 96. Note that the relative mass of one carbon-12 atom is taken as
1
exactly 12 units. So, the phrase 12 of the mass of carbon-12’ equals to 1 unit.
Answer: D
34
03 SPM CHEMISTRY F4.indd 34 27/02/2020 11:23 AM