Page 24 - APS(2022)_TG4 _Edisi Guru
P. 24
Sains
Infografik
BAB Daya dan Gerakan
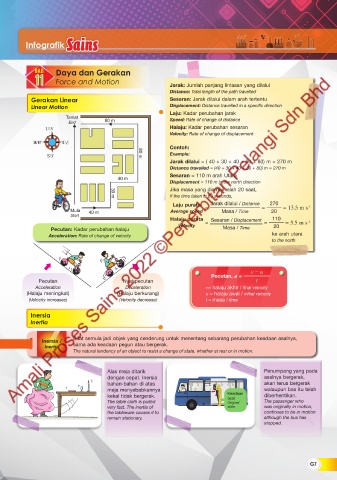
11 11 Force and Motion Jarak: Jumlah panjang lintasan yang dilalui
Distance: Total length of the path travelled
Gerakan Linear Sesaran: Jarak dilalui dalam arah tertentu
Linear Motion Displacement: Distance travelled in a specific direction
Laju: Kadar perubahan jarak
Tamat Speed: Rate of change of distance
End 80 m
Halaju: Kadar perubahan sesaran
Velocity: Rate of change of displacement
Contoh:
Example:
80 m
Jarak dilalui = ( 40 + 30 + 40 + 80 + 80) m = 270 m
Distance travelled = (40 + 30 + 40 + 80 + 80) m = 270 m
Sesaran = 110 m arah Utara
40 m
Displacement = 110 m in the north direction
Jika masa yang diambil ialah 20 saat,
If the time taken is 20 seconds,
30 m
Laju purata Jarak dilalui / Distance 270 -1
Mula 40 m Average speed = Masa / Time = 20 = 13.5 m s
Start
Halaju purata Sesaran / Displacement 110 -1
Velocity = = 20 = 5.5 m s
Pecutan: Kadar perubahan halaju Masa / Time
Acceleration: Rate of change of velocity ke arah utara
to the north
v − u
Pecutan, a =
Pecutan Nyahpecutan t
Acceleration Deceleration v= halaju akhir / final velocity
(Halaju meningkat) (Halaju berkurang) u = halaju awal / initial velocity
(Velocity increases) (Velocity decrease) t = masa / time
Inersia
Inertia
Sifat semula jadi objek yang cenderung untuk menentang sebarang perubahan keadaan asalnya,
Inersia /
Inertia sama ada keadaan pegun atau bergerak.
The natural tendency of an object to resist a change of state, whether at rest or in motion.
Alas meja ditarik Penumpang yang pada
dengan cepat. Inersia asalnya bergerak,
bahan-bahan di atas akan terus bergerak
meja menyebabkannya walaupun bas itu telah
kekal tidak bergerak. Keadaan diberhentikan.
asal
The table cloth is pulled Original The passenger who
very fast. The inertia of state was originally in motion,
the tableware causes it to continues to be in motion
remain stationary. although the bus has
stopped.
GPB G7
Infrografik APS Ting4.indd 7 26/07/2021 7:03 AM