Page 12 - Focus PT3 2020 Science ( BI Version )
P. 12
Science PT3 Chapter 2 Cell as the Basic Unit of Life
The Types and Functions of Animal Cells and Plant Cells
N
E
N
N
C
C
N
C
SC
SCIENCE INFO
SC
SC
E
E
SC
E
C
E
E
INFO
INFO
1. Humans, animals and plants are multicellular organisms in SC I I I I I E N C E INFO
INFO
E INFO
SCIENCE INFO
INFO
INFO
INFO
E INFO
INFO
INFO
INFO
large size, and they are made up of different types of cells for
various life processes. Humans are made up of Form
more than 50 trillion
2. These cells have different shapes and structures to carry out (50 000 000 000 000) cells.
Form
different functions. They are called specialised cells. 1
Specialised cells are cells that have become differentiated to carry out a particular function.
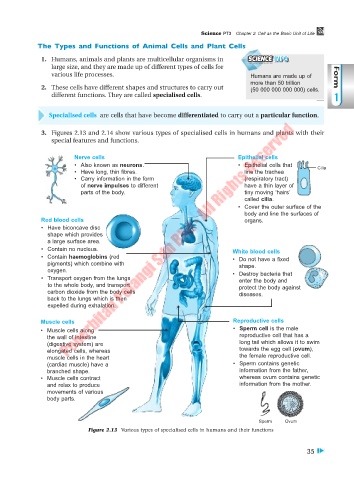
3. Figures 2.13 and 2.14 show various types of specialised cells in humans and plants with their
special features and functions.
Nerve cells Epithelial cells
• Also known as neurons. • Epithelial cells that
• Have long, thin fibres. line the trachea Cilia
• Carry information in the form (respiratory tract)
of nerve impulses to different have a thin layer of
parts of the body. tiny moving ‘hairs’
called cilia.
• Cover the outer surface of the
body and line the surfaces of
Red blood cells organs.
• Have biconcave disc
shape which provides
a large surface area.
• Contain no nucleus. White blood cells
• Contain haemoglobins (red • Do not have a fixed
pigments) which combine with shape.
oxygen. • Destroy bacteria that
• Transport oxygen from the lungs enter the body and
to the whole body, and transport protect the body against
carbon dioxide from the body cells diseases.
back to the lungs which is then
expelled during exhalation.
Muscle cells Reproductive cells
• Muscle cells along • Sperm cell is the male
the wall of intestine reproductive cell that has a
(digestive system) are long tail which allows it to swim
elongated cells, whereas towards the egg cell (ovum),
muscle cells in the heart the female reproductive cell.
(cardiac muscle) have a • Sperm contains genetic
branched shape. information from the father,
• Muscle cells contract whereas ovum contains genetic
and relax to produce information from the mother.
movements of various
body parts.
Sperm Ovum
Figure 2.13 Various types of specialised cells in humans and their functions
35
02 Fokus Science F1.indd 35 11/19/19 11:41 AM