Page 11 - Focus PT3 2020 Science ( BI Version )
P. 11
Science PT3 Chapter 2 Cell as the Basic Unit of Life
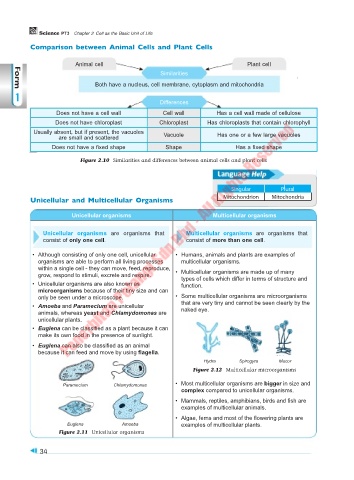
Comparison between Animal Cells and Plant Cells
Animal cell Plant cell
Similarities
Icon Focus KSSM Science form 1 English ver.
Both have a nucleus, cell membrane, cytoplasm and mitochondria
Form
Form
1
Differences
Does not have a cell wall Cell wall Has a cell wall made of cellulose
Plural
Does not have chloroplast Chloroplast Has chloroplasts that contain chlorophyll
Usually absent, but if present, the vacuoles Vacuole Has one or a few large vacuoles
are small and scattered
Does not have a fixed shape Shape Has a fixed shape
Figure 2.10 Similarities and differences between animal cells and plant cells
Singular Plural
Plural
Unicellular and Multicellular Organisms Mitochondrion Mitochondria
Unicellular organisms Multicellular organisms
Unicellular organisms are organisms that Multicellular organisms are organisms that
consist of only one cell. consist of more than one cell.
• Although consisting of only one cell, unicellular • Humans, animals and plants are examples of
organisms are able to perform all living processes multicellular organisms.
within a single cell - they can move, feed, reproduce, • Multicellular organisms are made up of many
grow, respond to stimuli, excrete and respire. types of cells which differ in terms of structure and
• Unicellular organisms are also known as function.
microorganisms because of their tiny size and can
only be seen under a microscope. • Some multicellular organisms are microorganisms
• Amoeba and Paramecium are unicellular that are very tiny and cannot be seen clearly by the
animals, whereas yeast and Chlamydomonas are naked eye.
unicellular plants.
• Euglena can be classified as a plant because it can
make its own food in the presence of sunlight.
• Euglena can also be classified as an animal
because it can feed and move by using flagella.
Hydra Spirogyra Mucor
Figure 2.12 Multicellular microorganisms
Paramecium Chlamydomonas • Most multicellular organisms are bigger in size and
complex compared to unicellular organisms.
• Mammals, reptiles, amphibians, birds and fish are
examples of multicellular animals.
• Algae, ferns and most of the flowering plants are
Euglena Amoeba examples of multicellular plants.
Figure 2.11 Unicellular organisms
34
02 Fokus Science F1.indd 34 11/19/19 11:41 AM