Page 18 - Ranger SPM 2022 - Additional Mathematics
P. 18
Additional Mathematics SPM Chapter 2 Quadratic Functions
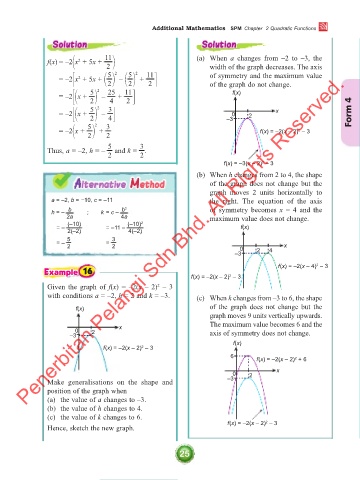
Solution Solution
f(x) = –2 x + 5x + 11 (a) When a changes from –2 to –3, the
2
2
width of the graph decreases. The axis
5
5
Penerbitan Pelangi Sdn Bhd. All Rights Reserved.
2
= –2 x + 5x + 2 + 11 of symmetry and the maximum value
–
2
2
2
2
of the graph do not change.
= –2 x + 5 2 – 25 + 11 f(x)
2
4
2
= –2 x + 5 2 – 3 –3 0 2 x Form 4
4
2
= –2 x + 5 2 + 3 f(x) = –2(x – 2) – 3
2
2
2
5 3
Thus, a = –2, h = – and k = .
2 2
2
f(x) = –3(x – 2) – 3
(b) When h changes from 2 to 4, the shape
Alternative Method of the graph does not change but the
graph moves 2 units horizontally to
a = –2, b = −10, c = –11 the right. The equation of the axis
h = – b ; k = c – b 2 of symmetry becomes x = 4 and the
2a 4a maximum value does not change.
(–10) (–10) 2
= – 2(–2) = –11 – 4(–2) f(x)
5 3
= – = x
2
2
–3 0 2 4
f(x) = –2(x – 4) – 3
2
Example 16
f(x) = –2(x – 2) – 3
2
Given the graph of f(x) = –2(x – 2) – 3
2
with conditions a = –2, h = 2 and k = –3. (c) When k changes from –3 to 6, the shape
f(x) of the graph does not change but the
graph moves 9 units vertically upwards.
x The maximum value becomes 6 and the
0 2
–3 axis of symmetry does not change.
f(x)
f(x) = –2(x – 2) – 3
2
6 f(x) = –2(x – 2) + 6
2
x
0 2
Make generalisations on the shape and –3
position of the graph when
(a) the value of a changes to –3.
(b) the value of h changes to 4.
(c) the value of k changes to 6. 2
Hence, sketch the new graph. f(x) = –2(x – 2) – 3
25
02 Ranger Add Mathematics Tg4.indd 25 25/02/2022 9:10 AM