Page 65 - Technology and Innovation Journal - 19-1
P. 65
EVENT ANALYTICS FOR INNOVATION 403
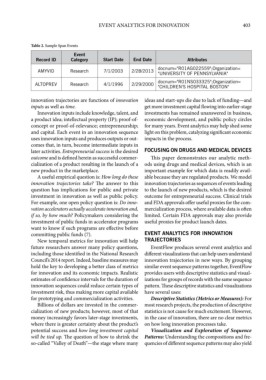
Table 2. Sample Span Events
Event
Record ID Category Start Date End Date Attributes
docnum="R01AG022559";Organization=
AMYVID Research 7/1/2003 2/28/2013
"UNIVERSITY OF PENNSYLVANIA"
docnum="R01NS033325";Organization=
ALTOPREV Research 4/1/1996 2/29/2000
"CHILDREN'S HOSPITAL BOSTON"
innovation trajectories are functions of innovation ideas and start-ups die due to lack of funding—and
inputs as well as time. get more investment capital flowing into earlier-stage
Innovation inputs include knowledge, talent, and investments has remained unanswered in business,
a product idea; intellectual property (IP); proof-of- economic development, and public policy circles
concept or proof-of-relevance; entrepreneurship; for many years. Event analytics may help shed some
and capital. Each event in an innovation sequence light on this problem, catalyzing significant economic
uses innovation inputs and produces outputs or out- impacts in the process.
comes that, in turn, become intermediate inputs in
later activities. Entrepreneurial success is the desired FOCUSING ON DRUGS AND MEDICAL DEVICES
outcome and is defined herein as successful commer- This paper demonstrates our analytic meth-
cialization of a product resulting in the launch of a ods using drugs and medical devices, which is an
new product in the marketplace. important example for which data is readily avail-
A useful empirical question is: How long do these able because they are regulated products. We model
innovation trajectories take? The answer to this innovation trajectories as sequences of events leading
question has implications for public and private to the launch of new products, which is the desired
investment in innovation as well as public policy. outcome for entrepreneurial success. Clinical trials
For example, one open policy question is: Do inno- and FDA approvals offer useful proxies for the com-
vation accelerators actually accelerate innovation and, mercialization process, where available data is often
if so, by how much? Policymakers considering the limited. Certain FDA approvals may also provide
investment of public funds in accelerator programs useful proxies for product launch dates.
want to know if such programs are effective before
committing public funds (7). EVENT ANALYTICS FOR INNOVATION
New temporal metrics for innovation will help TRAJECTORIES
future researchers answer many policy questions, EventFlow produces several event analytics and
including those identified in the National Research different visualizations that can help users understand
Council’s 2014 report. Indeed, baseline measures may innovation trajectories in new ways. By grouping
hold the key to developing a better class of metrics similar event sequence patterns together, EventFlow
for innovation and its economic impacts. Realistic provides users with descriptive statistics and visual-
estimates of confidence intervals for the duration of izations for groups of records with the same sequence
innovation sequences could reduce certain types of pattern. These descriptive statistics and visualizations
investment risk, thus making more capital available have several uses:
for prototyping and commercialization activities. Descriptive Statistics (Metrics or Measures): For
Billions of dollars are invested in the commer- most research projects, the production of descriptive
cialization of new products; however, most of that statistics is not cause for much excitement. However,
money increasingly favors later-stage investments, in the case of innovation, there are no clear metrics
where there is greater certainty about the product’s on how long innovation processes take.
potential success and how long investment capital Visualization and Exploration of Sequence
will be tied up. The question of how to shrink the Patterns: Understanding the compositions and fre-
so-called “Valley of Death”—the stage where many quencies of different sequence patterns may also yield