Page 261 - MARSIUM'21 COMP OF PAPER
P. 261
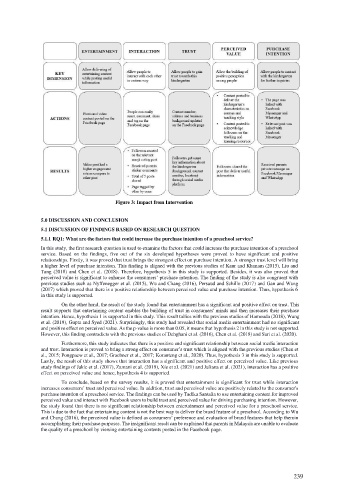
Figure 3: Impact from Intervention
5.0 DISCUSSION AND CONCLUSION
5.1 DISCUSSION OF FINDINGS BASED ON RESEARCH QUESTION
5.1.1 RQ1: What are the factors that could increase the purchase intention of a preschool service?
In this study, the first research question is used to examine the factors that could increase the purchase intention of a preschool
service. Based on the findings, five out of the six developed hypotheses were proved to have significant and positive
relationships. Firstly, it was proved that trust brings the strongest effect on purchase intention. A stronger trust level will bring
a higher level of purchase intention. This finding is aligned with the previous studies of Kaur and Khanam (2015), Liu and
Tang (2018) and Chen et al. (2018). Therefore, hypothesis 5 in this study is supported. Besides, it was also proved that
perceived value is significant to enhance the consumers’ purchase intention. The finding of the study is also congruent with
previous studies such as Nyffenegger et al. (2015), Wu and Chang (2016), Persaud and Schillo (2017) and Gan and Wang
(2017) which proved that there is a positive relationship between perceived value and purchase intention. Thus, hypothesis 6
in this study is supported.
On the other hand, the result of the study found that entertainment has a significant and positive effect on trust. This
result supports that entertaining content enables the building of trust in consumers' minds and then increases their purchase
intention. Hence, hypothesis 1 is supported in this study. This result tallies with the previous studies of Hamouda (2018), Wang
et al. (2019), Gupta and Syed (2021). Surprisingly, this study had revealed that social media entertainment had no significant
and positive effect on perceived value. As the p-value is more than 0.05, it means that hypothesis 2 in this study is not supported.
However, this finding contradicts with the previous studies of Dehghani et al. (2016), Chen et al. (2018) and Sari et al. (2020).
Furthermore, this study indicates that there is a positive and significant relationship between social media interaction
and trust. Interaction is proved to bring a strong effect on consumer’s trust which is aligned with the previous studies (Chen et
al., 2015; Pongpaew et al., 2017; Graebner et al., 2017; Koranteng et al., 2020). Thus, hypothesis 3 in this study is supported.
Lastly, the result of this study shows that interaction has a significant and positive effect on perceived value. Like previous
study findings of Jakic et al. (2017), Zamani et al. (2019), Xie et al. (2021) and Juliana et al. (2021), interaction has a positive
effect on perceived value and hence, hypothesis 4 is supported.
To conclude, based on the survey results, it is proved that entertainment is significant for trust while interaction
increases consumers’ trust and perceived value. In addition, trust and perceived value are positively related to the consumer's
purchase intention of a preschool service. The findings can be used by Tadika Santalia to use entertaining content for improved
perceived value and interact with Facebook users to build trust and perceived value for driving purchasing intention. However,
the study found that there is no significant relationship between entertainment and perceived value for a preschool service.
This is due to the fact that entertaining content is not the best way to deliver the brand feature of a preschool. According to Wu
and Chang (2016), the perceived value is defined as consumers’ preference and evaluation of brand features that help them in
accomplishing their purchase purposes. The insignificant result can be explained that parents in Malaysia are unable to evaluate
the quality of a preschool by viewing entertaining contents posted in the Facebook page.
239