Page 360 - MARSIUM'21 COMP OF PAPER
P. 360
339 Ali & Ahmad (2018)
higher interactivity on user satisfaction, value, and overall attitude in an e-commerce purchasing program by experimentally adjusting
interactivity using numerous elements such as chat and feedback forms. As Sutcliffe (2005) found, interactive metaphors have a
favourable impact on consumers' perceptions of website design. Higher levels of involvement were also found to have an effect on both
the website and the product or service in question, according to a separate study (Xu & Sundar, 2014). Based on the explanation above,
the researchers hypothesize:
H4: KKKL Express’s website interactivity will have a strong influence on user satisfaction.
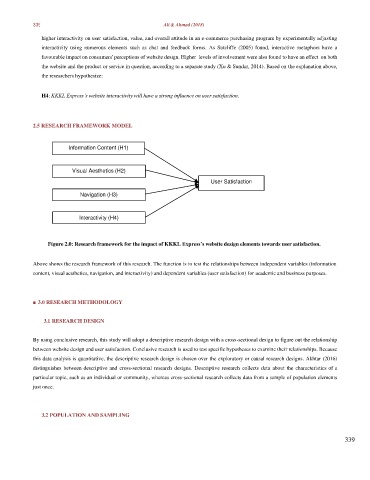
2.5 RESEARCH FRAMEWORK MODEL
Information Content (H1)
Visual Aesthetics (H2)
User Satisfaction
Navigation (H3)
Interactivity (H4)
Figure 2.0: Research framework for the impact of KKKL Express’s website design elements towards user satisfaction.
Above shows the research framework of this research. The function is to test the relationships between independent variables (information
content, visual aesthetics, navigation, and interactivity) and dependent variables (user satisfaction) for academic and business purposes.
■ 3.0 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
3.1 RESEARCH DESIGN
By using conclusive research, this study will adopt a descriptive research design with a cross-sectional design to figure out the relationship
between website design and user satisfaction. Conclusive research is used to test specific hypotheses to examine their relationships. Because
this data analysis is quantitative, the descriptive research design is chosen over the exploratory or causal research designs. Akhtar (2016)
distinguishes between descriptive and cross-sectional research designs. Descriptive research collects data about the characteristics of a
particular topic, such as an individual or community, whereas cross-sectional research collects data from a sample of population elements
just once.
3.2 POPULATION AND SAMPLING
339