Page 408 - MARSIUM'21 COMP OF PAPER
P. 408
2.5.4 Overall Brand Equity and Purchase Intention
In the case of purchase intention, consumers tend to prefer a better-known brand over a less-known brand (Choedon & Lee, 2020). The
role of brand equity in consumers' purchase decisions has been researched for a long time. Most of the studies found that customers buy
items not just for the functional value of the products or product quality but also for the value of the brand and the symbolic product
significance embedded in the product (Aji et al., 2020). Previous research has demonstrated that higher brand equity would positively and
significantly affect a consumer's purchase intention toward that brand (Pappu & Quester, 2017). According to Suryadi (2015), brand equity
(perceived quality, brand loyalty, brand awareness, brand association) has an essential simultaneous impact on purchase intention. Besides,
Perera et al. (2019) and Dissabandara (2020) previously showed that purchase intention is significantly affected by brand equity. Thus, the
hypothesis is proposed:
H4: Overall brand equity will have a positive and significant effect on purchase intention of telecommunication services.
2.6 RESEARCH FRAMEWORK
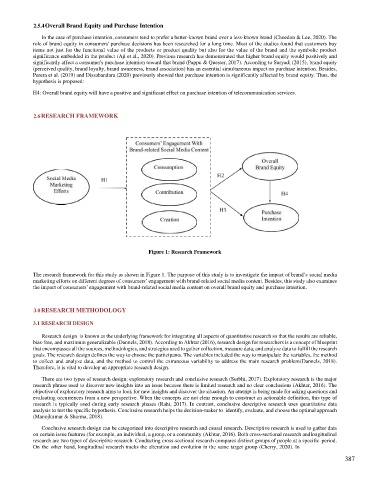
Figure 1: Research Framework
The research framework for this study as shown in Figure 1. The purpose of this study is to investigate the impact of brand’s social media
marketing efforts on different degrees of consumers’ engagement with brand-related social media content. Besides, this study also examines
the impact of consumers’ engagement with brand-related social media content on overall brand equity and purchase intention.
3.0 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
3.1 RESEARCH DESIGN
Research design is known as the underlying framework for integrating all aspects of quantitative research so that the results are reliable,
bias-free, and maximum generalizable (Dannels, 2018). According to Akhtar (2016), research design for researchers is a concept of blueprint
that encompasses all the sources, methodologies, and strategies used to gather collection, measure data, and analyze data to fulfill the research
goals. The research design defines the way to choose the participants. The variables included the way to manipulate the variables, the method
to collect and analyze data, and the method to control the extraneous variability to address the main research problem (Dannels, 2018).
Therefore, it is vital to develop an appropriate research design.
There are two types of research design: exploratory research and conclusive research (Surbhi, 2017). Exploratory research is the major
research phrase used to discover new insights into an issue because there is limited research and no clear conclusions (Akhtar, 2016). The
objective of exploratory research aims to look for new insights and discover the situation. An attempt is being made for asking questions and
evaluating occurrences from a new perspective. When the concepts are not clear enough to construct an actionable definition, this type of
research is typically used during early research phases (Rahi, 2017). In contrast, conclusive descriptive research uses quantitative data
analysis to test the specific hypothesis. Conclusive research helps the decision-maker to identify, evaluate, and choose the optimal approach
(Manojkumar & Sharma, 2018).
Conclusive research design can be categorized into descriptive research and causal research. Descriptive research is used to gather data
on certain issue features (for example, an individual, a group, or a community (Akhtar, 2016). Both cross-sectional research and longitudinal
research are two types of descriptive research. Conducting cross-sectional research compares distinct groups of people at a specific period.
On the other hand, longitudinal research tracks the alteration and evolution in the same target group (Cherry, 2020). In
387