Page 159 - Account 10
P. 159
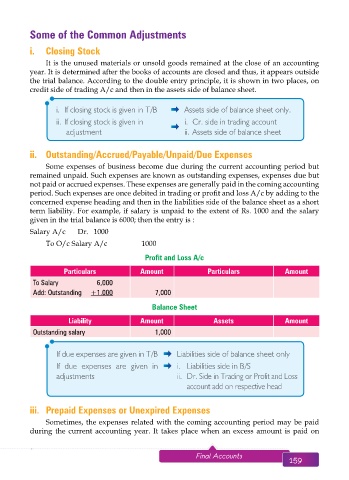
Some of the Common Adjustments
i. Closing Stock
It is the unused materials or unsold goods remained at the close of an accounting
year. It is determined after the books of accounts are closed and thus, it appears outside
the trial balance. According to the double entry principle, it is shown in two places, on
credit side of trading A/c and then in the assets side of balance sheet.
i. If closing stock is given in T/B Assets side of balance sheet only.
ii. If closing stock is given in i. Cr. side in trading account
adjustment ii. Assets side of balance sheet
ii. Outstanding/Accrued/Payable/Unpaid/Due Expenses
Some expenses of business become due during the current accounting period but
remained unpaid. Such expenses are known as outstanding expenses, expenses due but
not paid or accrued expenses. These expenses are generally paid in the coming accounting
period. Such expenses are once debited in trading or profit and loss A/c by adding to the
concerned expense heading and then in the liabilities side of the balance sheet as a short
term liability. For example, if salary is unpaid to the extent of Rs. 1000 and the salary
given in the trial balance is 6000; then the entry is :
Salary A/c Dr. 1000
To O/c Salary A/c 1000
Profit and Loss A/c
Particulars Amount Particulars Amount
To Salary 6,000
Add: Outstanding +1.000 7,000
Balance Sheet
Liability Amount Assets Amount
Outstanding salary 1,000
If due expenses are given in T/B Liabilities side of balance sheet only
If due expenses are given in i. Liabilities side in B/S
adjustments ii. Dr. Side in Trading or Profit and Loss
account add on respective head
iii. Prepaid Expenses or Unexpired Expenses
Sometimes, the expenses related with the coming accounting period may be paid
during the current accounting year. It takes place when an excess amount is paid on
158 Aakar’s Office Practice and Accountancy - 10 Final Accounts 159