Page 206 - Health, Population and Environment Education 9
P. 206
A. Male Reproductive System
The network of all organs, their structure and functions which are related for the
reproduction process in males is called male reproductive system.
Male reproductive system is designed in such a way that one organ produces numerous
minute spermatozoa (sperm cells). Another stores them and nourishes them. Then another
organ transfers them into female reproductive organ.
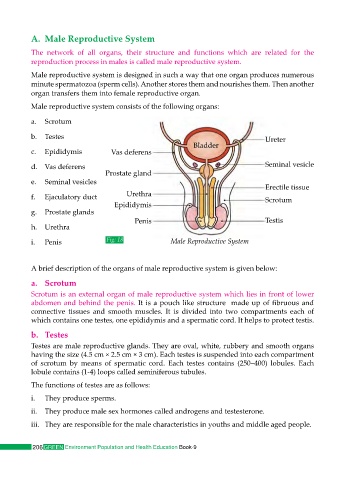
Male reproductive system consists of the following organs:
a. Scrotum
b. Testes Ureter
Bladder
c. Epididymis Vas deferens
d. Vas deferens Seminal vesicle
Prostate gland
e. Seminal vesicles
Erectile tissue
f. Ejaculatory duct Urethra Scrotum
Epididymis
g. Prostate glands
Penis Testis
h. Urethra
i. Penis Fig: 18 Male Reproductive System
A brief description of the organs of male reproductive system is given below:
a. Scrotum
Scrotum is an external organ of male reproductive system which lies in front of lower
abdomen and behind the penis. It is a pouch like structure made up of fibruous and
connective tissues and smooth muscles. It is divided into two compartments each of
which contains one testes, one epididymis and a spermatic cord. It helps to protect testis.
b. Testes
Testes are male reproductive glands. They are oval, white, rubbery and smooth organs
having the size (4.5 cm × 2.5 cm × 3 cm). Each testes is suspended into each compartment
of scrotum by means of spermatic cord. Each testes contains (250–400) lobules. Each
lobule contains (1-4) loops called seminiferous tubules.
The functions of testes are as follows:
i. They produce sperms.
ii. They produce male sex hormones called androgens and testesterone.
iii. They are responsible for the male characteristics in youths and middle aged people.
206 GREEN Environment Population and Health Education Book-9