Page 85 - leadership-experience-2008
P. 85
CikguOnline
CikguOnline
66 PART 2: RESEARCH PERSPECTIVES ON LEADERSHIP
Contingency approaches in this chapter. The contingency approaches seek to delineate the characteristics
approaches that seek to of situations and followers and examine the leadership styles that can be used
delineate the characteristics
of situations and followers and effectively. Assuming that a leader can properly diagnose a situation and muster
examine the leadership styles the fl exibility to behave according to the appropriate style, successful outcomes
that can be used effectively are highly likely.
Two basic leadership behaviors that can be adjusted to address various
contingencies are task behavior and relationship behavior, introduced in the previ-
ous chapter. Research has identified these two meta-categories, or broadly defi ned
behavior categories, as applicable to leadership in a variety of situations and time
3
periods. A leader can adapt his or her style to be high or low on both task and
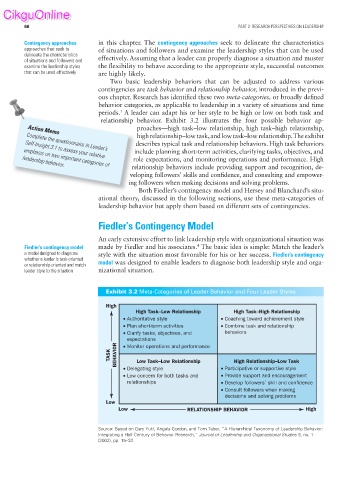
relationship behavior. Exhibit 3.2 illustrates the four possible behavior ap-
proaches—high task–low relationship, high task–high relationship,
Action Memo
high relationship–low task, and low task–low relationship. The exhibit
describes typical task and relationship behaviors. High task behaviors
Complete the questionnaire in Leader’s
include planning short-term activities, clarifying tasks, objectives, and
Self-Insight 3.1 to assess your relative
role expectations, and monitoring operations and performance. High
emphasis on two important categories of
leadership behavior.
relationship behaviors include providing support and recognition, de-
veloping followers’ skills and confidence, and consulting and empower-
ing followers when making decisions and solving problems.
Both Fiedler’s contingency model and Hersey and Blanchard’s situ-
ational theory, discussed in the following sections, use these meta-categories of
leadership behavior but apply them based on different sets of contingencies.
Fiedler’s Contingency Model
An early extensive effort to link leadership style with organizational situation was
4
Fiedler’s contingency model made by Fiedler and his associates. The basic idea is simple: Match the leader’s
a model designed to diagnose style with the situation most favorable for his or her success. Fiedler’s contingency
whether a leader is task-oriented
or relationship-oriented and match model was designed to enable leaders to diagnose both leadership style and orga-
leader style to the situation nizational situation.
Exhibit 3.2 Meta-Categories of Leader Behavior and Four Leader Styles
High
High Task–Low Relationship High Task–High Relationship
• Authoritative style • Coaching toward achievement style
• Plan short-term activities • Combine task and relationship
• Clarify tasks, objectives, and behaviors
expectations
• Monitor operations and performance
TASK BEHAVIOR Low Task–Low Relationship High Relationship–Low Task
• Delegating style • Participative or supportive style
• Low concern for both tasks and • Provide support and encouragement
relationships • Develop followers’ skill and confidence
• Consult followers when making
decisions and solving problems
Low
Low RELATIONSHIP BEHAVIOR High
Source: Based on Gary Yukl, Angela Gordon, and Tom Taber, “A Hierarchical Taxonomy of Leadership Behavior:
Integrating a Half Century of Behavior Research,” Journal of Leadership and Organizational Studies 9, no. 1
(2002), pp. 15–32.