Page 10 - ANUAL REPORT MOH 2017
P. 10
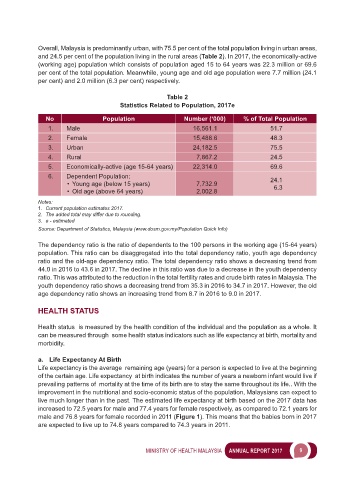
Overall, Malaysia is predominantly urban, with 75.5 per cent of the total population living in urban areas,
and 24.5 per cent of the population living in the rural areas (Table 2). In 2017, the economically-active
(working age) population which consists of population aged 15 to 64 years was 22.3 million or 69.6
per cent of the total population. Meanwhile, young age and old age population were 7.7 million (24.1
per cent) and 2.0 million (6.3 per cent) respectively.
Table 2
Statistics Related to Population, 2017e
No Population Number (‘000) % of Total Population
1. Male 16,561.1 51.7
2. Female 15,488.6 48.3
3. Urban 24,182.5 75.5
4. Rural 7,867.2 24.5
5. Economically-active (age 15-64 years) 22,314.0 69.6
6. Dependent Population: 24.1
• Young age (below 15 years) 7,732.9 6.3
• Old age (above 64 years) 2,002.8
Notes:
1. Current population estimates 2017.
2. The added total may differ due to rounding.
3. e - estimated
Source: Department of Statistics, Malaysia (www.dosm.gov.my/Population Quick Info)
The dependency ratio is the ratio of dependents to the 100 persons in the working age (15-64 years)
population. This ratio can be disaggregated into the total dependency ratio, youth age dependency
ratio and the old-age dependency ratio. The total dependency ratio shows a decreasing trend from
44.0 in 2016 to 43.6 in 2017. The decline in this ratio was due to a decrease in the youth dependency
ratio. This was attributed to the reduction in the total fertility rates and crude birth rates in Malaysia. The
youth dependency ratio shows a decreasing trend from 35.3 in 2016 to 34.7 in 2017. However, the old
age dependency ratio shows an increasing trend from 8.7 in 2016 to 9.0 in 2017.
HEALTH STATUS
Health status is measured by the health condition of the individual and the population as a whole. It
can be measured through some health status indicators such as life expectancy at birth, mortality and
morbidity.
a. Life Expectancy At Birth
Life expectancy is the average remaining age (years) for a person is expected to live at the beginning
of the certain age. Life expectancy at birth indicates the number of years a newborn infant would live if
prevailing patterns of mortality at the time of its birth are to stay the same throughout its life.. With the
improvement in the nutritional and socio-economic status of the population, Malaysians can expect to
live much longer than in the past. The estimated life expectancy at birth based on the 2017 data has
increased to 72.5 years for male and 77.4 years for female respectively, as compared to 72.1 years for
male and 76.8 years for female recorded in 2011 (Figure 1). This means that the babies born in 2017
are expected to live up to 74.8 years compared to 74.3 years in 2011.
MINISTRY OF HEALTH MALAYSIA ANNUAL REPORT 2017 9