Page 125 - ANUAL REPORT MOH 2017
P. 125
• Travel Advisory
The International Health Sector prepares and reviews the Travel Advisory information uploaded in the
Ministry of Health’s MyHEALTH Portal at the http://www.myhealth.gov.my/myhealth/. In addition, the
International Health Sector provides technical advice to the public on Travel Health enquiries through
MyHEALTH Portal from time to time.
Activities at International Points of Entry
i. Screening of Travellers Arriving from Countries with Risk of Yellow Fever Transmission
Malaysia is still free from Yellow Fever. However, this country has a high risk of acquiring this disease.
There are several routine activities implemented in this country in preventing Yellow Fever transmission,
such as Yellow Fever vaccination is requirement entry, screening at the International Points of Entry
and taking up quarantine measures and the activities as shown in Table 27.
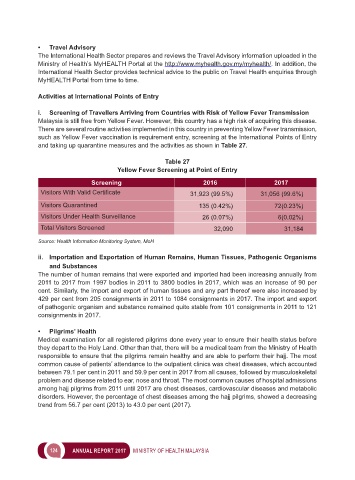
Table 27
Yellow Fever Screening at Point of Entry
Screening 2016 2017
Visitors With Valid Certificate 31,923 (99.5%) 31,056 (99.6%)
Visitors Quarantined 135 (0.42%) 72(0.23%)
Visitors Under Health Surveillance 26 (0.07%) 6(0.02%)
Total Visitors Screened 32,090 31,184
Source: Health Information Monitoring System, MoH
ii. Importation and Exportation of Human Remains, Human Tissues, Pathogenic Organisms
and Substances
The number of human remains that were exported and imported had been increasing annually from
2011 to 2017 from 1997 bodies in 2011 to 3800 bodies in 2017, which was an increase of 90 per
cent. Similarly, the import and export of human tissues and any part thereof were also increased by
429 per cent from 205 consignments in 2011 to 1084 consignments in 2017. The import and export
of pathogenic organism and substance remained quite stable from 101 consignments in 2011 to 121
consignments in 2017.
• Pilgrims’ Health
Medical examination for all registered pilgrims done every year to ensure their health status before
they depart to the Holy Land. Other than that, there will be a medical team from the Ministry of Health
responsible to ensure that the pilgrims remain healthy and are able to perform their hajj. The most
common cause of patients’ attendance to the outpatient clinics was chest diseases, which accounted
between 79.1 per cent in 2011 and 59.9 per cent in 2017 from all causes, followed by musculoskeletal
problem and disease related to ear, nose and throat. The most common causes of hospital admissions
among hajj pilgrims from 2011 until 2017 are chest diseases, cardiovascular diseases and metabolic
disorders. However, the percentage of chest diseases among the hajj pilgrims, showed a decreasing
trend from 56.7 per cent (2013) to 43.0 per cent (2017).
124 ANNUAL REPORT 2017 MINISTRY OF HEALTH MALAYSIA