Page 127 - ANUAL REPORT MOH 2017
P. 127
The 2017 report on National Health and Morbidity Survey (NHMS) on Maternal and Child Health findings
generally confirm the MoH administrative data on the coverage of maternal health care, i.e. antenatal
coverage (99 per cent), safe delivery (99.5 per cent) and postnatal visit at 1 month (98.2 per cent).
FAMILY PLANNING SERVICES
The Ministry of Health provides a wide range of contraceptive methods to cater for the different needs
and suitability of woman. The most popular contraceptive method used in year 2017 was contraceptive
pill (48.1 per cent) followed by progestogen-only injection (36.6 per cent), male condoms (8.2 per cent)
and intrauterine device (2.9 per cent). The total of new family planning acceptors in 2017 was 115,760
and the number of active users was 337,913.
The use of family planning among high risk women was monitored using two indicators, i.e. practice
indicator (percentage of high risk female clients who practised effective methods of contraceptive for 2
years) and quality indicator (percentage of those who continue practising family planning after 2 years).
The targets are 80 per cent and 70 per cent, respectively. In 2017 the practice indicator was 83.9 per
cent and quality indicator for cohort 2015-2017 was 79. 8 per cent.
MATERNAL DEATH
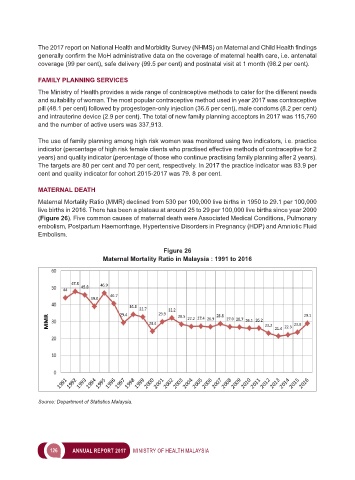
Maternal Mortality Ratio (MMR) declined from 530 per 100,000 live births in 1950 to 29.1 per 100,000
live births in 2016. There has been a plateau at around 25 to 29 per 100,000 live births since year 2000
(Figure 26). Five common causes of maternal death were Associated Medical Conditions, Pulmonary
embolism, Postpartum Haemorrhage, Hypertensive Disorders in Pregnancy (HDP) and Amniotic Fluid
Embolism.
Figure 26
Maternal Mortality Ratio in Malaysia : 1991 to 2016
Source: Department of Statistics Malaysia.
126 ANNUAL REPORT 2017 MINISTRY OF HEALTH MALAYSIA