Page 129 - ANUAL REPORT MOH 2017
P. 129
UNDER-5 MORTALITY, INFANT MORTALITY AND NEONATAL MORTALITY
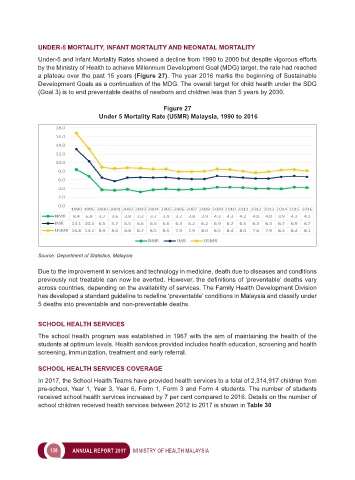
Under-5 and Infant Mortality Rates showed a decline from 1990 to 2000 but despite vigorous efforts
by the Ministry of Health to achieve Millennium Development Goal (MDG) target, the rate had reached
a plateau over the past 15 years (Figure 27). The year 2016 marks the beginning of Sustainable
Development Goals as a continuation of the MDG. The overall target for child health under the SDG
(Goal 3) is to end preventable deaths of newborn and children less than 5 years by 2030.
Figure 27
Under 5 Mortality Rate (U5MR) Malaysia, 1990 to 2016
Source: Department of Statistics, Malaysia
Due to the improvement in services and technology in medicine, death due to diseases and conditions
previously not treatable can now be averted. However, the definitions of ‘preventable’ deaths vary
across countries, depending on the availability of services. The Family Health Development Division
has developed a standard guideline to redefine ‘preventable’ conditions in Malaysia and classify under
5 deaths into preventable and non-preventable deaths.
SCHOOL HEALTH SERVICES
The school health program was established in 1967 with the aim of maintaining the health of the
students at optimum levels. Health services provided includes health education, screening and health
screening, immunization, treatment and early referral.
SCHOOL HEALTH SERVICES COVERAGE
In 2017, the School Health Teams have provided health services to a total of 2,314,917 children from
pre-school, Year 1, Year 3, Year 6, Form 1, Form 3 and Form 4 students. The number of students
received school health services increased by 7 per cent compared to 2016. Details on the number of
school children received health services between 2012 to 2017 is shown in Table 30
128 ANNUAL REPORT 2017 MINISTRY OF HEALTH MALAYSIA