Page 77 - Engineering Mathematics Workbook_Final
P. 77
Vector Calculus
3 3 (c) (x − x )( y − y
x + y x − 2 y 2 0 2 1 2 1 )
2
153. f = x − y 2 . The
2 2
0 x − 2 y = 2 0 (d) ( y − y 1 ) + (x − x 1 )
2
2
directional derivative off at (0, 0) in the [GATE-11 (PI)]
4 3
direction of i + j is _______ 2 $ 2 $
5 5 156. ( ,F x y ) ( x= + xy ) a + ( y + xy ) a . It’s
x
y
line integral over the straight line from
154. Consider points P and Q in xy – plane
with P = (1, 0) and Q = (0, 1). The line (x, y) = (0, 2) to (2, 0) evaluates to
integral 2 Q (xdx + ydy ) along the (a) -8 (b) 4
P (c) 8 (d) 0
semicircle with the line segment PQ as
its diameter [GATE-2009-EE]
(a) is -1 157. A path AB in the form of one quarter of
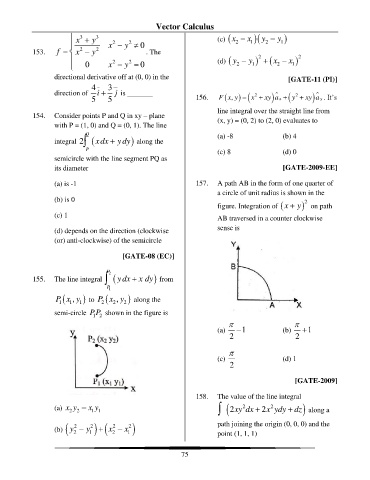
a circle of unit radius is shown in the
(b) is 0 2
figure. Integration of (x + ) y on path
(c) 1 AB traversed in a counter clockwise
(d) depends on the direction (clockwise sense is
(or) anti-clockwise) of the semicircle
[GATE-08 (EC)]
P
2
155. The line integral ( ydx x dy+ ) from
P 1
)
P 1 ( , x y to ( , y 2 ) along the
P x
2
1
2
1
semi-circle PP shown in the figure is
1 2
(a) − 1 (b) + 1
2 2
(c) (d) 1
2
[GATE-2009]
158. The value of the line integral
+
(a) x y − x y ( 2xy dx + 2 2x ydy dz ) along a
2
1 1
2 2
(b) ( 2 2 2 2 path joining the origin (0, 0, 0) and the
x −
+
y − y 1 ) ( 2 x 1 ) point (1, 1, 1)
2
75