Page 229 - DK Children's Encyclopedia
P. 229
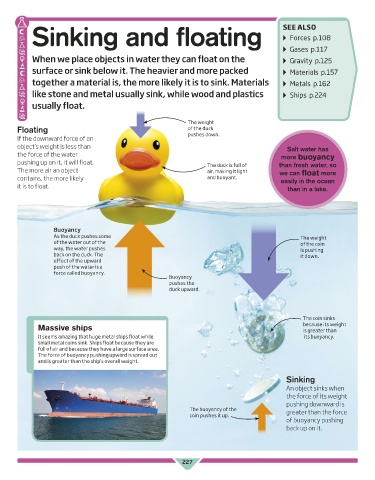
Sinking and floating SEE ALSO
▸ ▸ Forces p.108
▸ ▸ Gases p.117
When we place objects in water they can float on the ▸ ▸ Gravity p.125
surface or sink below it. The heavier and more packed ▸ ▸ Materials p.157
together a material is, the more likely it is to sink. Materials ▸ ▸ Metals p.162
like stone and metal usually sink, while wood and plastics ▸ ▸ Ships p.224
usually float.
The weight
Floating of the duck
If the downward force of an pushes down.
object’s weight is less than Salt water has
the force of the water more buoyancy
pushing up on it, it will float. The duck is full of than fresh water, so
The more air an object air, making it light we can float more
contains, the more likely and buoyant. easily in the ocean
it is to float. than in a lake.
Buoyancy
As the duck pushes some The weight
of the water out of the of the coin
way, the water pushes is pushing
back on the duck. The it down.
effect of the upward
push of the water is a
force called buoyancy.
Buoyancy
pushes the
duck upward.
The coin sinks
Massive ships because its weight
is greater than
It seems amazing that huge metal ships float while its buoyancy.
small metal coins sink. Ships float because they are
full of air and because they have a large surface area.
The force of buoyancy pushing upward is spread out
and is greater than the ship’s overall weight.
Sinking
An object sinks when
the force of its weight
pushing downward is
The buoyancy of the greater than the force
coin pushes it up.
of buoyancy pushing
back up on it.
227
US_227_Sinking_and_floating.indd 227 16/05/2017 12:11