Page 43 - Drug Discovery and Development: Prospects and Challenges
P. 43
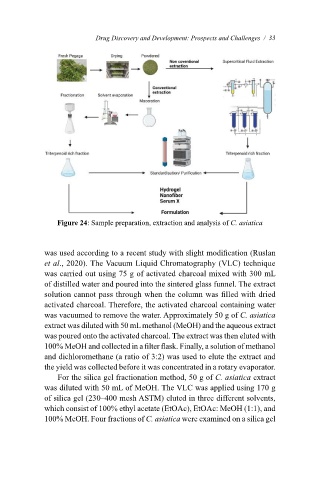
and evaporated using a rotary evaporator to obtain the extract in powder form (Figure 24) (Azis et al.,
2017; Ahmed et al., 2019).
The non-conventional extraction method was also performed using the supercritical fluid
extraction, which was screened using the two-level factorial design and optimised through the Central
Composite Design (CCD) method by altering three factors (co-solvent percentage, pressure, and
temperature) on the asiaticoside content. The model obtained was used to optimise the extraction
Drug Discovery and Development: Prospects and Challenges / 33
process C. asiatica to obtain a higher yield of asiaticoside fraction (Ruslan et al., 2020).
Figure 24: Sample preparation, extraction and analysis of C. asiatica
Figure 24: Sample preparation, extraction and analysis of C. asiatica
Optimisation of Fractionation
was used according to a recent study with slight modification (Ruslan
Two fractionation methods were performed for the optimisation of pegaga extract, which is the
et al., 2020). The Vacuum Liquid Chromatography (VLC) technique
fractionation using activated charcoal and fractionation using silica gel. In the first fractionation,
was carried out using 75 g of activated charcoal mixed with 300 mL
activated charcoal was used according to a recent study with slight modification (Ruslan et al., 2020).
of distilled water and poured into the sintered glass funnel. The extract
The Vacuum Liquid Chromatography (VLC) technique was carried out using 75 g of activated
solution cannot pass through when the column was filled with dried
charcoal mixed with 300 mL of distilled water and poured into the sintered glass funnel. The extract
activated charcoal. Therefore, the activated charcoal containing water
solution cannot pass through when the column was filled with dried activated charcoal. Therefore, the
was vacuumed to remove the water. Approximately 50 g of C. asiatica
extract was diluted with 50 mL methanol (MeOH) and the aqueous extract
37
was poured onto the activated charcoal. The extract was then eluted with
100% MeOH and collected in a filter flask. Finally, a solution of methanol
and dichloromethane (a ratio of 3:2) was used to elute the extract and
the yield was collected before it was concentrated in a rotary evaporator.
For the silica gel fractionation method, 50 g of C. asiatica extract
was diluted with 50 mL of MeOH. The VLC was applied using 170 g
of silica gel (230–400 mesh ASTM) eluted in three different solvents,
which consist of 100% ethyl acetate (EtOAc), EtOAc: MeOH (1:1), and
100% MeOH. Four fractions of C. asiatica were examined on a silica gel