Page 38 - Drug Discovery and Development: Prospects and Challenges
P. 38
China and Madagascar, C. asiatica has caught our attention to study its unique properties. The herb
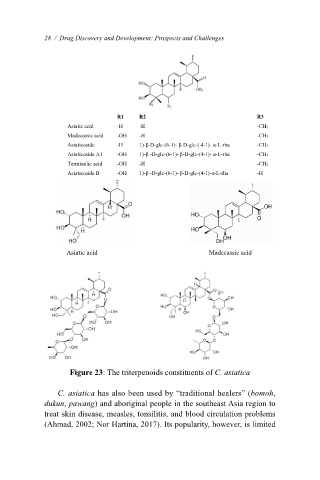
possesses active principles comprising triterpenoids, such as asiaticoside, madecassoside, and asiatic
acid (Figure 23). The huge attention on this plant is related to its activity on skin generation, boosting
memory, increasing concentration and alertness, and anti-stress. During the wound healing process, C.
asiatica stimulates collagen synthesis, which allows the skin to proliferate effectively.
28 / Drug Discovery and Development: Prospects and Challenges
R1 R2 R3
Asiatic acid -H -H -CH3
Madecassic acid -OH -H -CH3
Asiaticoside -H 1)-β-D-glc-(6-1)- β-D-glc-( 4-1)- α-L-rha -CH3
Asiaticoside A1 -OH 1)-β -D-glc-(6-1)- β-D-glc-(4-1)- α-L-rha -CH3
Terminolic acid -OH -H -CH3
Asiaticoside B -OH 1)-β -D-glc-(6-1)- β-D-glc-(4-1)-α-L-rha -H
Asiatic acid Madecassic acid
Figure 23: The triterpenoids constituents of C. asiatica
33
C. asiatica has also been used by “traditional healers” (bomoh,
dukun, pawang) and aboriginal people in the southeast Asia region to
treat skin disease, measles, tonsilitis, and blood circulation problems
(Ahmad, 2002; Nor Hartina, 2017). Its popularity, however, is limited