Page 44 - digitalliteracy
P. 44
2.1 Which Hardware Is Right for You?
Consider Speed, Processing Power, Memory, and Storage Space
You may have heard people use terms like kilobits, kilobytes, megabits, or megabytes when
they talk about computers. Both bits and bytes are units of measurement in computer lan-
guage, and they determine the speed and processing power of computer devices, as well as
the memory and storage capacity of electronic devices.
Bits are measurements of the speed at which the computer performs calculations or transfers
data. For example, a computer may have a 32-bit or 64-bit processor, or an Internet service
provider may advertise that it offers download speeds of 60 megabits per second (abbrevi-
ated Mbits per second or Mbps). Generally, the more bits per second, the faster and more
powerful the device. Bytes (pronounced “bites”) are measurements of the size or capacity
of a computer file and the computer memory or storage devices. For example, you may have
a computer that has a 500-gigabyte hard drive to store data. Generally, the more bytes, the
greater a computer file’s size or the computer data storage’s capacity. Because the term bytes
is used most frequently to describe computer hardware, a handy reference chart of the names,
sizes, and abbreviations of bytes is provided in Table 2.1.
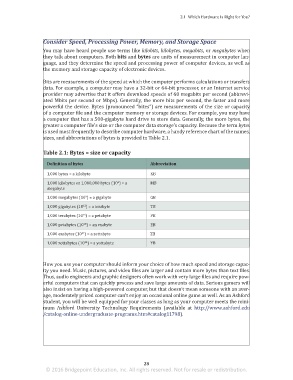
Table 2.1: Bytes = size or capacity
Definition of bytes Abbreviation
1,000 bytes = a kilobyte KB
6
1,000 kilobytes or 1,000,000 bytes (10 ) = a MB
megabyte
9
1,000 megabytes (10 ) = a gigabyte GB
12
1,000 gigabytes (10 ) = a terabyte TB
15
1,000 terabytes (10 ) = a petabyte PB
18
1,000 petabytes (10 ) = an exabyte EB
21
1,000 exabytes (10 ) = a zettabyte ZB
24
1,000 zettabytes (10 ) = a yottabyte YB
How you use your computer should inform your choice of how much speed and storage capac-
ity you need. Music, pictures, and video files are larger and contain more bytes than text files.
Thus, audio engineers and graphic designers often work with very large files and require pow-
erful computers that can quickly process and save large amounts of data. Serious gamers will
also insist on having a high-powered computer, but that doesn’t mean someone with an aver-
age, moderately priced computer can’t enjoy an occasional online game as well. As an Ashford
student, you will be well equipped for your classes as long as your computer meets the mini-
mum Ashford University Technology Requirements (available at http://www.ashford.edu
/catalog-online-undergraduate-programs.htm#catalog11798).
28
© 2016 Bridgepoint Education, Inc. All rights reserved. Not for resale or redistribution.
sol82612_02_m02_021-046.indd 28 6/29/16 5:11 PM