Page 141 - text book form physics kssm 2020
P. 141
Chapter 4
Heat
Solving Problems Involving Specifi c Heat Capacity
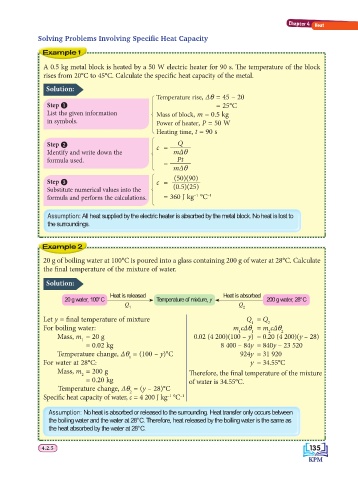
Example 1
A 0.5 kg metal block is heated by a 50 W electric heater for 90 s. Th e temperature of the block
rises from 20°C to 45°C. Calculate the specifi c heat capacity of the metal.
Solution:
Temperature rise, Δθ = 45 – 20
Step = 25°C
List the given information 14243 Mass of block, m = 0.5 kg
in symbols. Power of heater, P = 50 W
Heating time, t = 90 s
Step c = Q
Identify and write down the 14243 mΔθ
formula used. Pt
=
mΔθ
(50)(90)
Step c =
Substitute numerical values into the 14243 (0.5)(25)
–1
formula and perform the calculations. = 360 J kg °C –1
Assumption: All heat supplied by the electric heater is absorbed by the metal block. No heat is lost to
the surroundings.
Example 2
20 g of boiling water at 100°C is poured into a glass containing 200 g of water at 28°C. Calculate
the fi nal temperature of the mixture of water.
Solution:
Heat is released Heat is absorbed
20 g water, 100°C Temperature of mixture, y 200 g water, 28°C
Q Q
1 2
Let y = fi nal temperature of mixture Q = Q 2
1
For boiling water: m cΔθ = m cΔθ
1 1 2 2
Mass, m = 20 g 0.02 (4 200)(100 – y) = 0.20 (4 200)(y – 28)
1
= 0.02 kg 8 400 – 84y = 840y – 23 520
Temperature change, Δθ = (100 – y)°C 924y = 31 920
1
For water at 28°C: y = 34.55°C
Mass, m = 200 g
2 Th erefore, the fi nal temperature of the mixture
= 0.20 kg of water is 34.55°C.
Temperature change, Δθ = (y – 28)°C
2
Specifi c heat capacity of water, c = 4 200 J kg °C –1
–1
Assumption: No heat is absorbed or released to the surrounding. Heat transfer only occurs between
the boiling water and the water at 28°C. Therefore, heat released by the boiling water is the same as
the heat absorbed by the water at 28°C.
135
4.2.5 135
4.2.5