Page 144 - text book form physics kssm 2020
P. 144
Specifi c latent heat of fusion, l of a substance is the
f File
quantity of heat, Q that is absorbed during melting or the
quantity of heat released during freezing of 1 kg of the substance Based on the Kinetic Theory of
without any change in temperature. Matter, the higher the average
Specifi c latent heat of vaporisation, l of a substance is kinetic energy of a molecule, the
v
the quantity of heat, Q that is absorbed during boiling or the higher the temperature of the
quantity of heat released during condensation of 1 kg of the object. Latent heat absorbed
substance without any change in temperature. during melting and boiling
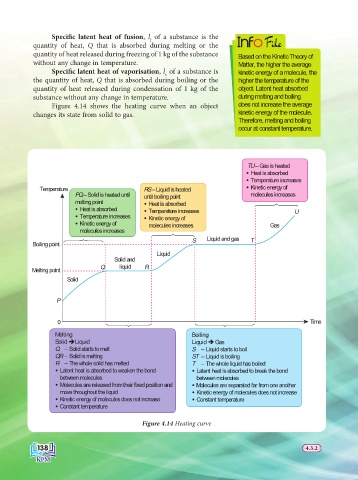
Figure 4.14 shows the heating curve when an object does not increase the average
changes its state from solid to gas. kinetic energy of the molecule.
Therefore, melting and boiling
occur at constant temperature.
TU – Gas is heated
Heat is absorbed
Temperature increases
Temperature RS – Liquid is heated Kinetic energy of
PQ – Solid is heated until until boiling point molecules increases
melting point Heat is absorbed
Heat is absorbed Temperature increases U
Temperature increases Kinetic energy of
Kinetic energy of molecules increases Gas
molecules increases
S Liquid and gas T
Boiling point
Liquid
Solid and
Q liquid R
Melting point
Solid
P
0 Time
Melting Boiling
Solid ÎLiquid Liquid Î Gas
Q – Solid starts to melt S – Liquid starts to boil
QR – Solid is melting ST – Liquid is boiling
R – The whole solid has melted T – The whole liquid has boiled
Latent heat is absorbed to weaken the bond Latent heat is absorbed to break the bond
between molecules between molecules
Molecules are released from their fixed position and Molecules are separated far from one another
move throughout the liquid Kinetic energy of molecules does not increase
Kinetic energy of molecules does not increase Constant temperature
Constant temperature
Figure 4.14 Heating curve
138
138 4.3.2
138
138
4.3.2