Page 183 - text book form physics kssm 2020
P. 183
Chapter 5
Waves
File
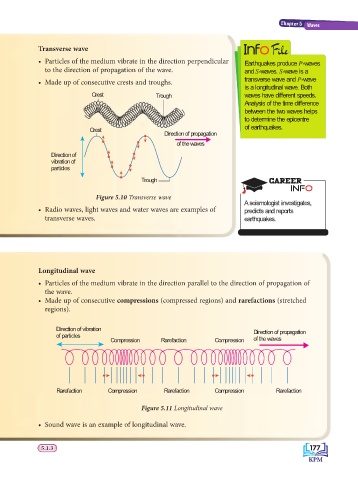
Transverse wave
• Particles of the medium vibrate in the direction perpendicular Earthquakes produce P-waves
to the direction of propagation of the wave. and S-waves. S-wave is a
transverse wave and P-wave
• Made up of consecutive crests and troughs.
is a longitudinal wave. Both
Crest Trough waves have different speeds.
Analysis of the time difference
between the two waves helps
to determine the epicentre
Crest of earthquakes.
Direction of propagation
of the waves
Direction of
vibration of
particles
Trough CAREER
iNFO
Figure 5.10 Transverse wave
A seismologist investigates,
• Radio waves, light waves and water waves are examples of predicts and reports
transverse waves. earthquakes.
Longitudinal wave
• Particles of the medium vibrate in the direction parallel to the direction of propagation of
the wave.
• Made up of consecutive compressions (compressed regions) and rarefactions (stretched
regions).
Direction of vibration Direction of propagation
of particles
Compression Rarefaction Compression of the waves
Rarefaction Compression Rarefaction Compression Rarefaction
Figure 5.11 Longitudinal wave
• Sound wave is an example of longitudinal wave.
177
177
177
5.1.3
5.1.3 177