Page 34 - Ultimate Visual Dictionary (DK)
P. 34
THE UNIVERSE
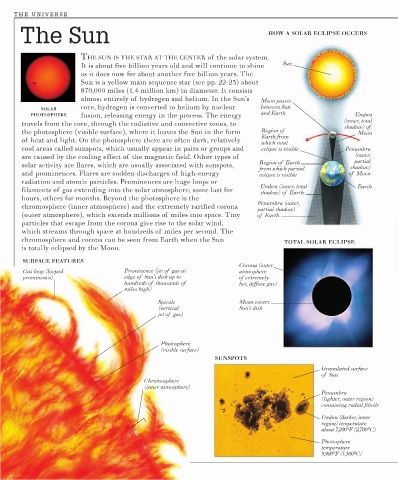
The Sun HOW A SOLAR ECLIPSE OCCURS
THE SUN IS THE STAR AT THE CENTER of the solar system.
Sun
It is about five billion years old and will continue to shine
as it does now for about another five billion years. The
Sun is a yellow main sequence star (see pp. 22-23) about
870,000 miles (1.4 million km) in diameter. It consists
almost entirely of hydrogen and helium. In the Sun’s Moon passes
core, hydrogen is converted to helium by nuclear between Sun
SOLAR
and Earth
PHOTOSPHERE fusion, releasing energy in the process. The energy Umbra
(inner, total
travels from the core, through the radiative and convective zones, to shadow) of
the photosphere (visible surface), where it leaves the Sun in the form Region of Moon
Earth from
of heat and light. On the photosphere there are often dark, relatively which total
cool areas called sunspots, which usually appear in pairs or groups and eclipse is visible Penumbra
are caused by the cooling effect of the magnetic field. Other types of (outer,
Region of Earth partial
solar activity are flares, which are usually associated with sunspots,
from which partial shadow)
and prominences. Flares are sudden discharges of high-energy eclipse is visible of Moon
radiation and atomic particles. Prominences are huge loops or
Umbra (inner, total Earth
filaments of gas extending into the solar atmosphere; some last for shadow) of Earth
hours, others for months. Beyond the photosphere is the
Penumbra (outer,
chromosphere (inner atmosphere) and the extremely rarified corona partial shadow)
(outer atmosphere), which extends millions of miles into space. Tiny of Earth
particles that escape from the corona give rise to the solar wind,
which streams through space at hundreds of miles per second. The
chromosphere and corona can be seen from Earth when the Sun
TOTAL SOLAR ECLIPSE
is totally eclipsed by the Moon.
SURFACE FEATURES
Corona (outer
Gas loop (looped Prominence (jet of gas at atmosphere
prominence) edge of Sun’s disk up to of extremely
hundreds of thousands of hot, diffuse gas)
miles high)
Spicule Moon covers
(vertical Sun’s disk
jet of gas)
Photosphere
(visible surface)
SUNSPOTS
Granulated surface
of Sun
Chromosphere
(inner atmosphere)
Penumbra
(lighter, outer region)
containing radial fibrils
Umbra (darker, inner
region) temperature
about 7,200°F (2,700°C)
Photosphere
temperature
9,900°F (5,500°C)