Page 31 - Ultimate Visual Dictionary (DK)
P. 31
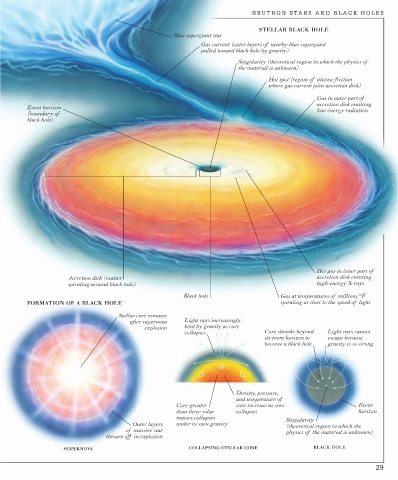
NEUTRON STARS AND BLACK HOLES
STELLAR BLACK HOLE
Blue supergiant star
Gas current (outer layers of nearby blue supergiant
pulled toward black hole by gravity)
Singularity (theoretical region in which the physics of
the material is unknown)
Hot spot (region of intense friction
where gas current joins accretion disk)
Gas in outer part of
accretion disk emitting
Event horizon low-energy radiation
(boundary of
black hole)
Hot gas in inner part of
Accretion disk (matter accretion disk emitting
spiraling around black hole) high-energy X-rays
Black hole Gas at temperatures of millions °F
FORMATION OF A BLACK HOLE spiraling at close to the speed of light
Stellar core remains
after supernova Light rays increasingly
explosion bent by gravity as core
collapses Core shrinks beyond Light rays cannot
its event horizon to escape because
become a black hole gravity is so strong
Density, pressure,
and temperature of
Core greater core increase as core Event
than three solar collapses horizon
masses collapses Singularity
Outer layers under its own gravity (theoretical region in which the
of massive star
physics of the material is unknown)
thrown off in explosion
SUPERNOVA COLLAPSING STELLAR CORE BLACK HOLE
29