Page 290 - (DK) The Ultimate Visual Dictionary 2nd Ed.
P. 290
GEOLOGY, GEOGRAPHY, AND METEOROLOGY
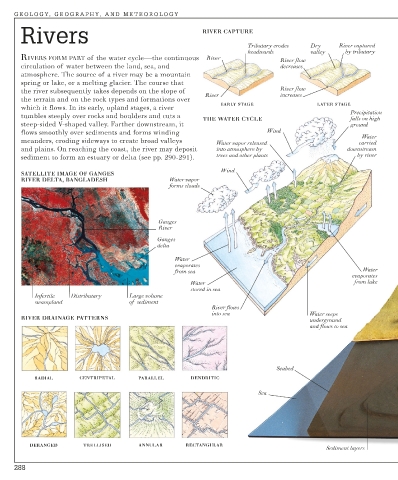
Rivers RIVER CAPTURE
Tributary erodes Dry River captured
headwards valley by tributary
RIVERS FORM PART of the water cycle—the continuous River
River flow
circulation of water between the land, sea, and decreases
atmosphere. The source of a river may be a mountain
spring or lake, or a melting glacier. The course that
the river subsequently takes depends on the slope of River flow
River increases
the terrain and on the rock types and formations over
EARLY STAGE LATER STAGE
which it flows. In its early, upland stages, a river
Precipitation
tumbles steeply over rocks and boulders and cuts a
THE WATER CYCLE falls on high
steep-sided V-shaped valley. Farther downstream, it ground
flows smoothly over sediments and forms winding Wind
Water
meanders, eroding sideways to create broad valleys Water vapor released carried
and plains. On reaching the coast, the river may deposit into atmosphere by downstream
sediment to form an estuary or delta (see pp. 290-291). trees and other plants by river
Wind
SATELLITE IMAGE OF GANGES
RIVER DELTA, BANGLADESH Water vapor
forms clouds
Ganges
River
Ganges
delta
Water
evaporates
Water
from sea
evaporates
Water from lake
stored in sea
Infertile Distributary Large volume
swampland of sediment
River flows
into sea Water seeps
RIVER DRAINAGE PATTERNS underground
and flows to sea
Seabed
RADIAL CENTRIPETAL PARALLEL DENDRITIC
Sea
DERANGED TRELLISED ANNULAR RECTANGULAR
Sediment layers
288