Page 292 - (DK) The Ultimate Visual Dictionary 2nd Ed.
P. 292
GEOLOGY, GEOGRAPHY, AND METEOROLOGY
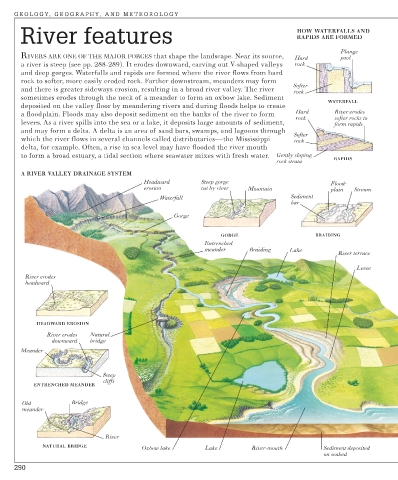
River features HOW WATERFALLS AND
RAPIDS ARE FORMED
Plunge
RIVERS ARE ONE OF THE MAJOR FORCES that shape the landscape. Near its source, Hard pool
a river is steep (see pp. 288-289). It erodes downward, carving out V-shaped valleys rock
and deep gorges. Waterfalls and rapids are formed where the river flows from hard
rock to softer, more easily eroded rock. Farther downstream, meanders may form
Softer
and there is greater sideways erosion, resulting in a broad river valley. The river rock
sometimes erodes through the neck of a meander to form an oxbow lake. Sediment
WATERFALL
deposited on the valley floor by meandering rivers and during floods helps to create
a floodplain. Floods may also deposit sediment on the banks of the river to form Hard River erodes
rock softer rocks to
levees. As a river spills into the sea or a lake, it deposits large amounts of sediment, form rapids
and may form a delta. A delta is an area of sand bars, swamps, and lagoons through
Softer
which the river flows in several channels called distributaries—the Mississippi rock
delta, for example. Often, a rise in sea level may have flooded the river mouth
to form a broad estuary, a tidal section where seawater mixes with fresh water. Gently sloping
rock strata RAPIDS
A RIVER VALLEY DRAINAGE SYSTEM
Headward Steep gorge Flood-
erosion cut by river Mountain plain Stream
Waterfall Sediment
bar
Gorge
GORGE BRAIDING
Entrenched
meander Braiding Lake
River terrace
Levee
River erodes
headward
HEADWARD EROSION
River erodes Natural
downward bridge
Meander
Steep
cliffs
ENTRENCHED MEANDER
Old Bridge
meander
River
NATURAL BRIDGE
Oxbow lake Lake River-mouth Sediment deposited
on seabed
290